Question
Question: The area of cross-section of the wider tube shown in figure is \[\;900\,c{m^2}\]. If the boy standin...
The area of cross-section of the wider tube shown in figure is 900cm2. If the boy standing on the piston weights 45kg, the difference in the levels of water in the tubes.
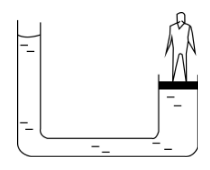
Solution
The force applied perpendicular to an object's surface per unit area over which the force is spread is known as pressure. The pressure gauges in relation to the atmospheric pressure is known as gauge pressure. Pressure is measured in a variety of ways.
Complete answer:
A piston can be used in reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders, and pneumatic cylinders, among other things. It's the moving part that's contained by a cylinder and sealed shut by piston rings. The object of a piston rod and/or connecting rod in an engine is to pass force from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crankshaft.
The mechanism is inverted in a pump, with energy transmitted from the crankshaft to the piston to compress or expel the fluid in the cylinder. The piston may also serve as a valve in some engines by covering and uncovering ports in the cylinder. We know that at level AB,
P1=P2......(equi pressure surface)
hρg=Amg
⇒h=Aρm
Now to find A (Cross sectional area)
A=900cm2⇒A=10000900m2⇒A=0.09m2
To find Weight of the body
m=45×9.8N=441N
Hence the pressure below the boy = =0.09441=4900N/m2
From this one can conclude that pressure due to the difference of water column is also 4900N/m2.
Let the difference of water column be X.
Hence, 1000×9.8×X=4900
X=1000×9.84900⇒X=0.5m∴X=50cm
Hence the difference in water levels is 50 cm.
Note: The elevation of the free surface of a sea, creek, lake, or reservoir relative to a given vertical datum is known as water level, gauge height, or point. Pressure Drops as Altitude Rises: As altitude rises, pressure drops. The average weight of the air above a unit area at any elevation can be perceived as pressure at any elevation. There are fewer air molecules above a given surface at higher elevations than at lower elevations.
