Question
Question: The answer to this question is a single digit integer, ranging from 0 to 9. The compressibility fa...
The answer to this question is a single digit integer, ranging from 0 to 9.
The compressibility factor Z for an ideal gas will be________.
Solution
Compressibility factor is the ratio of PV and nRT. For an ideal gas, we can say that PV=nRT. Both the sides of the equation satisfy equality. Ideal gases are assumed to follow all the gas laws.
Complete step by step answer:
- In order to answer this question, let us find out what is the difference between real gas and ideal gas. A gas which is expected to follow all the gas laws i.e Boyle’s law, Charles Law and Gay-Lussac’s law. Moreover, the gas particles are assumed to have negligible volume and also that they do not have any intermolecular forces of attraction between them. However, this is not true for the gases as there is variation of temperature and pressure.
- Compressibility factor is the factor which decides the extent of deviation of real gases from the ideal gas behaviour. Compressibility factor ‘Z’ is defined as the ratio of product PV to nRT, mathematically
Z=nRTPV, where P is pressure, V is volume, R is universal gas constant and T is temperature.
- Let us see the graph between compressibility factor over a range of pressure for different gases:
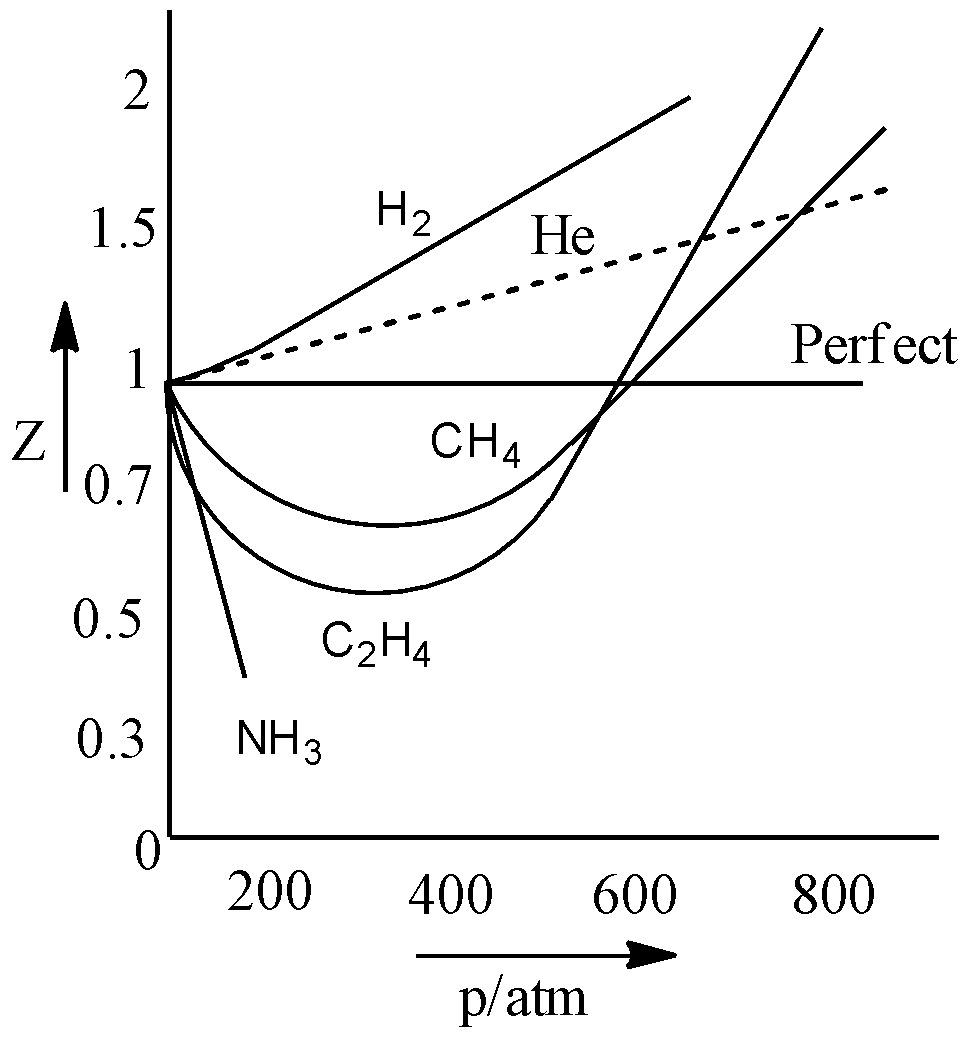
As can be seen from the graph, the compressibility factor of an ideal gas is 1, as the ratio of PV and nRT is equal to one. Hence, we obtain the integral answer as ‘1’.
Note:
| Compressibility Factor Z | Pressure | Compressibility |
|---|---|---|
| Z=1 | All | Normal |
| Z>1 | High | Difficult |
| Z<1 | Intermediate | Easy |
It should be noted that Z is almost equal to unity in a condition where pressure is low. Temperature is also an important factor which plays a role in changing the compressibility factor.
