Question
Question: The angle of intersection between the curves \[y=\left[ \left| \sin x \right|+\left| \cos x \right| ...
The angle of intersection between the curves y=[∣sinx∣+∣cosx∣] and x2+y2=10 , where x denote the greatest integer ≤x , is
A.tan−13
B. tan−1(−3)
C. tan−13
D. tan−1(−31)
Solution
We need to find the angle of intersection between the curves y=[∣sinx∣+∣cosx∣] and x2+y2=10 . For this first find the range of y=[∣sinx∣+∣cosx∣] . After that, we will be considering only the value of lower bound since x denotes the greatest integer ≤x ,i.e. y=1 . After that, substitute that value in x2+y2=10 . Find its slope by differentiating. Then get the next slope by differentiating y=1 . Now use the equation tanθ=1+m1m2m2−m1 to get the value of the angle.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to find the angle of intersection between the curves y=[∣sinx∣+∣cosx∣] and x2+y2=10 .
Let us find the range of y=[∣sinx∣+∣cosx∣] .
We know that the range of ∣sinx∣ is
0≤∣sinx∣≤1
And the range of ∣cosx∣ is
0≤∣cosx∣≤1
Therefore, range of y=[∣sinx∣+∣cosx∣] can be found out as follows:
y=sinx+cosxwherex∈(0,2π) .
Now multiply and divide RHS by 2 . So the above equation becomes,
y=2(21sinx+21cosx)...(i)
Now, sin(x+4π)=sinxcos4π+cosxsin4π
Solving, we get
sin(x+4π)=21sinx+21cosx
Therefore equation (i) can be written as
y=2sin(x+4π)
We know that sinx ranges from [−1,1] .
Therefore, −1≤sin(x+4π)≤1
Multiplying by 2 we get
−2≤2sin(x+4π)≤2
As ∣sinx∣ ranges from 0≤∣sinx∣≤1 , comparing with the above one, we get
y=[∣sinx∣+∣cosx∣]=[1,2]
It is given that x denote the greatest integer ≤x . So we will consider the value y=1 .
Given that x2+y2=10 . Substituting the value of y here, we get
x2+1=10⇒x2=9
x=±3
Therefore, the intersection points are q(3,1) and p(−3,1) .
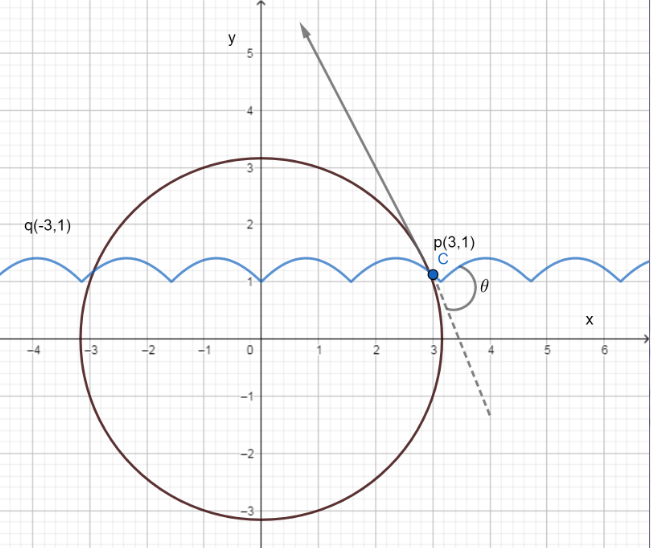
We need to find the slope of the tangent (±3,1) to x2+y2=10 .
Now differentiate x2+y2=10 with respect to x . We will get
2x+2ydxdy=0
⇒x+ydxdy=0
⇒dxdy=y−x
Now for the point q(3,1) ,
dxdyp(3,1)=−3
For the point p(−3,1) ,
dxdyp(−3,1)=3
Therefore, slope m1=±3 .
We have, y=1 .
Differentiating y with respect to x , we get
dxdyp=0
That is, the slope m2=dxdyp=0 .
Now, to find the angle of intersection, we have
tanθ=1+m1m2m2−m1
We will use in this case m2=−3 as per the figure.
Substituting the value, we will get
tanθ=1+0×−30−(−3)=∣3∣=±3
Taking inverse of tan we will get the value of θ .
Therefore, θ=tan−13 and θ=tan−1(−3) .
Hence the correct options are A and B.
Note:
In this question, it is not necessary to write the steps to get the range of y=[∣sinx∣+∣cosx∣] .
We know that when sinx increases cosx decreases. So the maximum value cannot be obtained.
We know that at x=4π both sinx and cosx will be the same, i.e, 21 .
So y=sinx+cosx=21+21=2 .
Therefore, the maximum value of y=[∣sinx∣+∣cosx∣]=2 .
To find the minimum value, we know that minimum value of sinx=0 and that of cosx=1 .
Now y=[∣sinx∣+∣cosx∣]=0+1=1 .
Thus the range of y=[∣sinx∣+∣cosx∣]=[1,2] .
