Question
Question: The angle of incidence in air for a light ray is 40 degrees. If the ray travels through water of ref...
The angle of incidence in air for a light ray is 40 degrees. If the ray travels through water of refractive index 4/3. Find the angle of refraction.
(sin40∘=0.643)
Solution
The relationship of angle of incidence and angle of refraction at interface of two media is given by Snell’s law. Snell’s law states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is equal to the reciprocal of the ratio of the indices of refraction.
Use Snell’s law to find the angle of refraction.
Formula used:
Law of refraction or Snell’s law, sinθ2sinθ1=(μ1μ2)
Complete step-by-step answer:
When a light wave passes at some angle from one medium to another medium, its direction changes. This phenomenon is referred to as refraction.
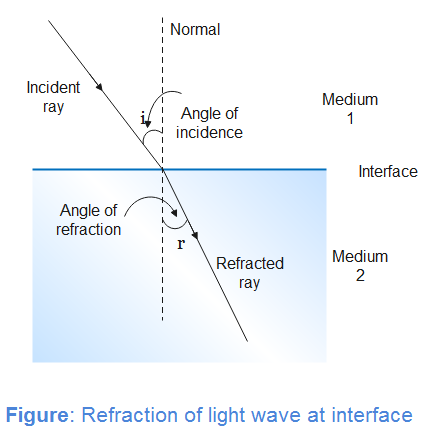
Angle of incidence is defined as the angle between incident ray and normal to the interface of the media and angle of refraction is the angle between refracted ray and normal as shown in figure.
Angle of incidence and angle of refraction are related by Snell’s law. Snell’s law states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is equal to the reciprocal of the ratio of the indices of refraction.
sinrsini=(μ1μ2)
We are given that angle of incidence i=40∘ refractive index of medium 2 which is water is μ2=34. We know that the refractive index of air is μ1=1. Substituting these values in Snell’s law, we have
sinrsin40∘=14/3
On rearranging and solving the above equation, we get
sinr=43sin40∘=43×0.643≈0.48
Therefore, angle of refraction is r=sin−1(0.48)
Note: The law of refraction or Snell’s law is valid for all pairs of media at the point of incidence. Incident ray, normal and refracted ray lie in the same plane.
Refractive index of a medium is a unitless quantity. It is also defined as the ratio of velocity of wave in the medium to velocity of wave in vacuum. Refractive index of air or free space is unity.
