Question
Question: The \( Al O {2} ^ {-} \) ion in aqueous solution exists as: (A) \( {{\left[ Al{{\left( OH \right)}...
The AlO2− ion in aqueous solution exists as:
(A) [Al(OH)4]−
(B) [Al(OH)4(H2O)]−
(C) [Al(OH)4(H2O)2]−
(D) [Al(OH)6]−
Solution
AlO2− is known as aluminate ion. In aqueous solution these ions are surrounded by four water molecules. The four hydroxyl groups are formed and these along with two water molecules are held together by the coordinate bond and a complex is formed.
Complete Step by Step Solution
The aluminate ion gets surrounded by four water molecules in aqueous solution. Two of the water molecules react with the oxygen present in aluminate ions and form four hydroxyl groups. Now these four hydroxyl groups and two molecules of water are held together by coordinate bond and they form a complex [Al(OH)4(H2O)2]− .
So, the correct option is (C).
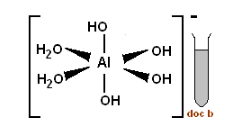
Aluminate is a polyatomic ion because it contains one aluminum atom and two oxygen atoms. This gives the whole ion a -1 oxidation state.
Additional Information
In the solvated state, an ion in a solution is surrounded by solvent molecules. Specific example of solvation is hydration, where the solvent is water. Coordinate covalent bonds are formed when one atom shares a lone pair of electrons resulting in bond formation. It is a type of covalent bond that is formed by sharing of an electron pair from a single atom rather than mutual sharing of an electron pair by two atoms.
Note
The aluminate ion forms a negative complex in aqueous solution. A negatively charged complex ion is called an anionic complex. An anion is a negatively charged ion. A complex is made up of a central metal atom surrounded by negatively charged ions or neutral molecules having a lone pair of electrons known as ligands. Examples of ligands are neutral water molecules, ammonia, carbon monoxide, etc.
