Question
Question: The addition of HBr is easiest with: (A) \(C{{H}_{2}}=CH-Cl\) (B) \(Cl-CH=CH-Cl\) (C) \(C{{H...
The addition of HBr is easiest with:
(A) CH2=CH−Cl
(B) Cl−CH=CH−Cl
(C) CH3−CH=CH2
(D) (CH3)2C=CH2
Solution
Stability of carbocation increases by the presence of electron donating groups around and more the number of alpha hydrogen atoms, more is the stability of carbocation, this undergoes by the process of hyperconjugation.
Complete answer:
Addition of hydrogen halide to alkene proceed through formation of carbocation.
A carbocation is a molecule in which a carbon atom has a positive charge and three bonds. We can basically say that they are carbon cations. Formerly, it was known as carbonium ion. Carbocation today is defined as any even-electron cation that possesses a significant positive charge on the carbon atom.
Carbocation gets stabilised by hyperconjugation and inductive effect, Increasing substitution, increases the hyperconjugation and thus it increases stability. More the hyperconjugation more is the stability.
R3C+ (3o ; most stable) > R2CH+ (2o ) > RCH2+ (1o) CH3+ (methyl; least stable)
Option A and B have Chlorine present in the compound, which is an electron withdrawing group and it destabilizes the carbocation formed.
Considering option C, the carbocation formed will be of secondary carbon and will have 6 alpha hydrogens. The structure of intermediate will be as follows:
CH3−CH+−CH3
Considering option D, the carbocation formed will be of tertiary carbon and will have 9 alpha hydrogens. The structure of intermediate will be as follows:
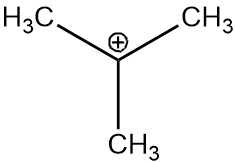
Therefore, the addition of HBr will be easiest with the D option.
Note:
Hyperconjugation is the stabilising interaction that results from the interaction of the electrons in a σ -bond (usually C-H or C-C) with an adjacent empty or partially filled p-orbital or a π -orbital to give an extended molecular orbital that increases the stability of the system.
