Question
Question: \(\text{ Xe}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}\text{ }\) on hydrolysis gives: A) \(\text{ Xe}{{\text{O}}_{\te...
XeF6 on hydrolysis gives:
A) XeO3
B) XeO2
C) XeO
D) Xe
Solution
The xenon hexafluoride is a xenon compound. The XeF6 undergoes the partial or complete hydrolysis reaction. Xenon hexafluoride on hydrolysis gives oxide as a product along with the hydrofluoric acid. The hydrolysis product is a strong oxidizing agent.
Complete Solution :
Xenon is a noble gas element. It is a fifth-period element. The electronic configuration of xenon is as shown below:
Xe = [Kr]4d10 5s2 5p6
- The valence shell of xenon contains 8 electrons. It also has an empty 5d orbital. The six fluorine atoms are bonded to the xenon atom through six covalent bonds and form a xenon hexafluoride compound. Xenon undergoes sp3d3 hybridization and has seven hybrid orbitals. Six hybrid orbitals form a covalent bond with six fluorine atoms and contain one lone pair of electrons.
The structure of xenon hexafluoride is as shown below:
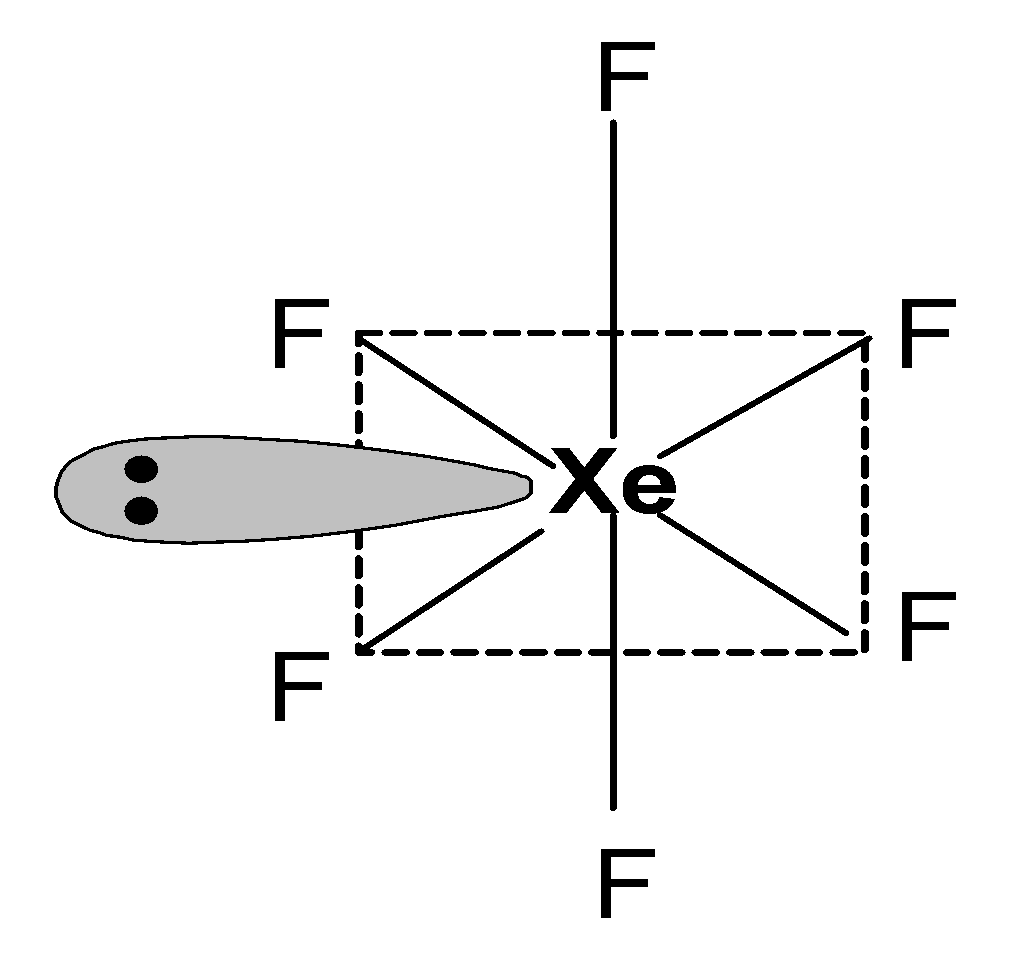
XeF6 is one of the three binary fluorides formed by xenon.
The xenon hexafluoride undergoes a complete hydrolysis reaction. The hydrolysis of XeF6 forms a xenon trioxide XeO3 and hydrofluoric acid HF .The reaction between the xenon hexafluoride and water is as shown below:
XeF6 + 3H2O → XeO3 + 6HF
The xenon trioxide is highly explosive in nature. It acts as a strong oxidizing agent in the solution.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Note that, the partial hydrolysis of XeF6 gives oxyfluorides such as XeOF4 and XeO2F2 . The reaction of partial hydrolysis of xenon hexafluoride is as follows:
\text{ }\left. \begin{aligned}
& \text{Xe}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}\text{ + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O }\to \text{ XeO}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ }+\text{ 2HF } \\\
& \text{ Xe}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}\text{ + 2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O }\to \text{ Xe}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{2}}\text{ }+\text{ 4HF} \\\
\end{aligned} \right\\}\text{ Partial hydrolysis }
