Question
Question: \[{\text{Phenol }}\xrightarrow[{{\text{oxid}}}]{{{\text{Aerial}}}}{\text{Coloured product}}\] This i...
Phenol AerialoxidColoured product This is due to the formation of :
E.
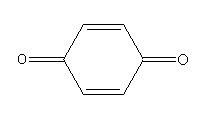
F.
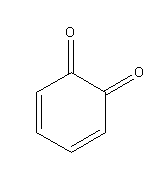
G.
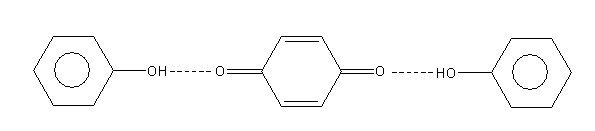
H. All
Solution
The reaction given to us is aerial oxidation of phenol. Oxidation of phenol in presence of air gives the colour product. The oxygen in the air reacts with phenol and gives quinone products.
Complete step by step answer: On exposure to air phenol slowly oxidises and turns to the p-benzoquinone product. The colour of the p-benzoquinone product is pink.
The oxidation reaction of phenol is as follows:
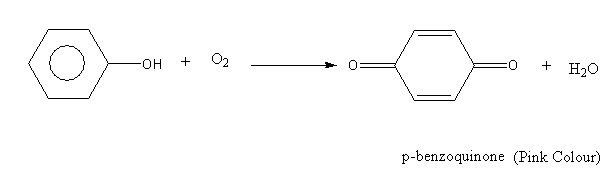
Here, phenol is aromatic while the p-benzoquinone is non-aromatic.
A p-benzoquinone form again reacts with a second molecule of phenol and gives the polymerized product of diphenoquinone which is red colour.
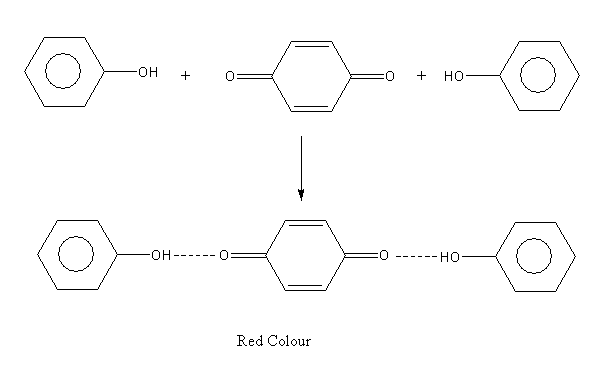
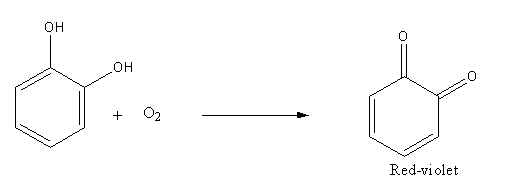
Oxidation of dihydroxybenzene (catechol) in presence of air produce 1,2-benzoquinone:
so (B) is the incorrect option.Thus, option (A) and (C) are the correct answer.
Additional Information:
Oxidation of phenol in the air gives colour compounds. When we store phenol in the air it turns to pink due to the formation of p-benzoquinone.
Catechol when stored in the air turns to red-violet due to the formation of 1, 2-benzoquinone.
Note: Oxidation is the addition of oxygen atoms. The phenol hydroxyl group is an electron-donating group that influences the nucleophilic character of phenol. Quinone's product is non-aromatic. In quinines carbonyl double bond is in conjugation with a double bond in the ring.
