Question
Question: \({\text{Ni(py}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{(Cl}}{{\text{O}}_4}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\) exists in...
Ni(py)4(ClO4)2 exists in a yellow diamagnetic form containing the cation [Ni(py)4]2+ and ClO4− ions, and a blue paramagnetic form containing trans [Ni(py)4(ClO4)2] molecules in which oxygen atoms for the ClO4− ions completed the octahedral coordination of the metal ions. The hybridization of nickel in the yellow and blue complexes respectively are:
A. sp3andd2sp3
B. dsp2andd2sp3
C. dsp2andsp3d2
D. sp3and sp3d2
Solution
The complex [Ni(py)4]2+ has four ligand so, nickel metal require four hybrid orbitals. The complex [Ni(py)4]2+ is diamagnetic means all the electrons of d-orbital of metal are paired. [Ni(py)4]2+. The complex [Ni(py)4(ClO4)2] has six ligand so, nickel metal require six hybrid orbitals. The complex [Ni(py)4(ClO4)2] is paramagnetic means nickel metal has some unpaired electrons.
Complete answer:
According to the valence bond theory, the orbitals of metals combine to form orbitals of the same energy. These orbitals are known as hybrid orbital. Each ligand donates an electron pair to a hybrid orbital.
Based on the number of electron pairs the hybridization and shape is determined.
Ni(py)4(ClO4)2exists as[Ni(py)4]2+and ClO4−ions. [Ni(py)4]2+is an a yellow diamagnetic complex.
Nickel ions have eight electrons in d-orbitals. [Ni(py)4]2+ is a diamagnetic complex it means the pairing of electrons in d-orbitals of nickel take place. Coordination number of nickel metal is four, so metal requires four hybridised orbitals to make four bonds with four pyridine ligands.
The hybridization in [Ni(py)4]2+ is shown as follows:
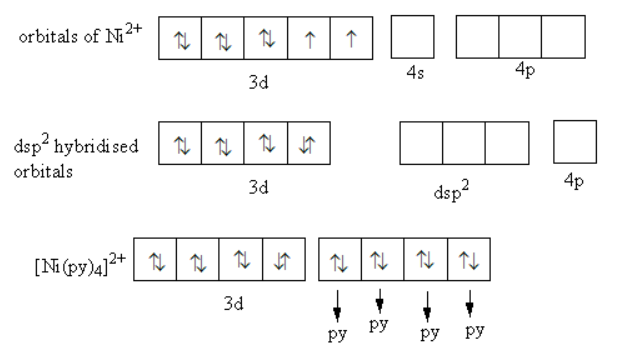
Eight electrons of nickel ion get paired in four d-orbitals. Remaining one d-orbital combines with one s and two p-orbitals to form four hybridised orbitals. So, the hybridization of nickel metal in [Ni(py)4]2+ is dsp2 .
Ni(py)4(ClO4)2 exists as trans [Ni(py)4(ClO4)2] molecules. [Ni(py)4(ClO4)2] is a blue paramagnetic octahedral complex. So, the coordination number of nickel metal is six so metal requires six hybridised orbitals to make six bonds with six ligands.
Nickel ions have eight electrons in d-orbitals. [Ni(py)4(ClO4)2] is a paramagnetic complex it means the electrons in d-orbitals of nickel do not pairs. The hybridization in [Ni(py)4(ClO4)2] is shown as follows:
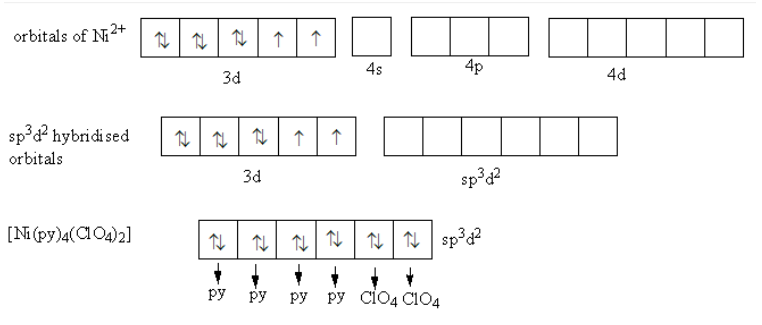
Due to unpaired electrons, [Ni(py)4(ClO4)2] is paramagnetic. No d-orbitals are available for the hybridization. So, one-s, three-p and two d-orbitals of outer 4 d-shell combines to form six hybridised orbitals. So, the hybridization of nickel metal in [Ni(py)4(ClO4)2] is $$$$ .
**Therefore, option (C) dsp2 and sp3d2 is correct.
Note:**
The orbitals of the central atom combine to form the hybrid orbitals. Ligand donates electron pairs in these hybrid orbitals. The number of hybrid orbitals depends upon the number of sigma bonds. The number of sigma bonds represents the type of hybridization. [Ni(py)4]2+ is diamagnetic. If it will be paramagnetic then no pairing will take place then the hybridization will be sp3 because in that case no d-orbital will be available for the hybridization. If [Ni(py)4(ClO4)2] will be diamagnetic then the hybridization will be d2sp3 .
