Question
Question: Test cross in Drosophila or plants involves crossing A. The \[{{F}_{1}}\] hybrid with a double rec...
Test cross in Drosophila or plants involves crossing
A. The F1 hybrid with a double recessive genotype
B. Between two genotypes with the dominant trait
C. Between two genotypes with the recessive trait
D. Between two F1 hybrids
Solution
A test cross is done to determine or check the genotype of resultant hybrids of the F1 generation. It is performed between the resultant hybrid of the first cross and usually the parent with traits that can be expressed only in homozygous condition. A large number of offspring is required for reliable results.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A test cross is defined as a cross between an organism having dominant traits and an organism with recessive traits. Simply a test cross is a cross between a hybrid of unknown genotype with dominant character and double recessive parent. The firs cross involving a homozygous dominant and a homozygous recessive produces F1 hybrids. These F1 hybrids will always have dominant characteristics. But to check whether the dominant character is homozygous or heterozygous the test-cross is performed. Homozygous refers to a condition in which both alleles have the same effect. For example, if two alleles for tallness are present together they are called homozygous tall. On the other hand, if an organism has one allele for tallness and another for the dwarfness together they are called heterozygous.
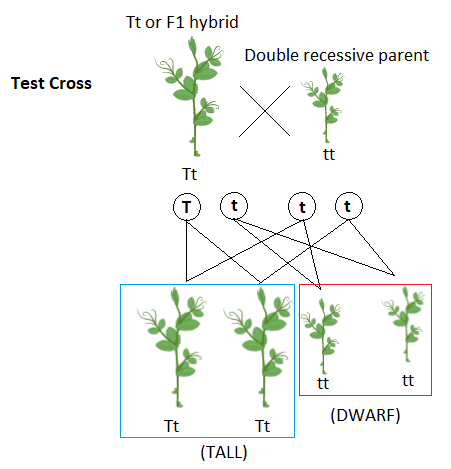
Let us understand the test cross through an example.
A homozygous tall plant with genotype TT and homozygous small plant with genotype tt is crossed to form F1 hybrids. Now, these F1 hybrids have tall height and the genotype is Tt. Now, to confirm the heterozygosity of the F1 hybrids, they will be crossed with a homozygous or double recessive parent. This resulted in the formation of half tall and half-dwarf progeny. This confirms that F1 generation was heterozygous dominant.
So, we can conclude from the above discussion, that the right answer is option A.
Note: The limitation of test cross is that a large number of progeny is required to confirm the results. The test cross is usually performed to check the type of dominant genotype. The dominant genotypes can be homozygous dominant or heterozygous dominant.
