Question
Question: Sulphuric acid provides a simple example of: (A) Coordinate bonds (B) Non-covalent compound (C...
Sulphuric acid provides a simple example of:
(A) Coordinate bonds
(B) Non-covalent compound
(C) Covalent ion
(D) Non-covalent ion
(E) None of these
Solution
Hint : The elements that are in and beyond the third period of the periodic table have 3d also available for bonding. Sulfuric acid is a compound with covalent bonds, since all the bonds are covalent.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Sulphur is the central atom in sulphuric acid( H2SO4 ), surrounded by oxygen atoms and hydrogen.
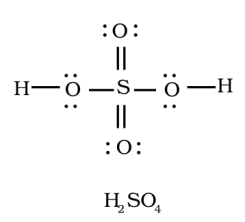
Atomic number of sulphur is 16 , it has 6 electrons in its outer shell. So it has 6 valence electrons. As sulphur has vacant d- orbitals it can show variable valencies.
Valency of oxygen is 2 , whereas of hydrogen it's 1 .
The total number of electron pairs are determined by dividing the total valence electrons by two.
Sulphuric acid has 32 valence electrons which implies 16 electron pairs.
The sulphur will form a double bond with oxygen as shown in the above diagram.
The bonding between the atoms is by sharing the electrons.
Therefore, sulfuric acid is a compound with covalent, since all the bonds are covalent.
But Sulphuric acid is a very strong acid, it completely ionizes into hydronium( H3O+ ) and hydrogen sulfate ions ( HSO4− ) in aqueous solution.
H2SO4 is an ionic compound but it has covalent bonds.
Therefore from the above conclusion we can easily conclude that Sulphuric acid has covalent bonds but it ionizes readily making it a very strong acid.
The option D which is Sulphuric acid having non covalent ions is correct.
Note :
Many sites claim Sulphuric acid to have coordinate bonds, which is insignificant to debate currently. The bonds that loosely hold hydrogen are very weak and ionic. Therefore the hydrogen ion is easily separated from the molecular lattice in aqueous solution.
