Question
Question: Study the given pedigree chart and answer the question that follows. Is the trait sex-linked or a...
Study the given pedigree chart and answer the question that follows.
Is the trait sex-linked or autosomal?
Solution
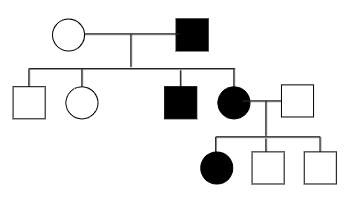
A pedigree is a way of analyzing the inheritance pattern of a trait within a family. The circle represents the female and the square represents the male. The darkened square represents a male with the trait to be studied. The sex-linked trait can be recognized by criss-cross inheritance and autosomal can be recognized by normal Mendelian inheritance.
Complete answer: Pedigree charts are a way to understand the inheritance history of a family. It also allows us to know the future inheritance pattern of a particular trait. Pedigree charts are diagrams that exhibit the occurrence and appearance of traits of a particular gene from one generation to the next. A pedigree chart can simply be referred to as a ‘family tree’. A standardized set of symbols represents the parents and their future generations. The males are typically represented by squares and females by circles. The horizontal line represents the cross. The vertical line represents the progeny and the horizontal line between progeny represents siblings. The dark circle or square represents the individual with the trait being studied. Now, in the given pedigree chart, the male carries the trait to be studied. The progeny produced by parents represents the first generation. We can see that the first generation consists of half the progeny carrying the trait and half not carrying the trait. This characteristic is representative of the fact that the trait is heterozygous. If the trait is sex-linked, then there will be a criss-cross pattern of inheritance. This means that from the father the trait will pass on to his daughters only. But this is not the case and we can conclude that it is not a sex-linked trait. The trait shown in the given pedigree chart is autosomal as it is inherited by both daughter and son and is passed on to grand-daughter. Also, the trait is dominant as one parent carrying the trait is enough to pass it on to future generations. Hence, we can conclude that the trait is autosomal dominant.
Note: The other autosomal dominant diseases are Huntington’s disease, tuberous sclerosis, hypercholesterolemia, etc. Huntington's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by disturbed mental abilities. If the normal repeat section of Huntington’s gene gets elongated by mutation it causes the production of mutant proteins. A single parent carrying the mutation is enough to cause the disease.
