Question
Question: Structure of \({N_2}O\) is similar to that of \(C{O_2}\) . A. True B. False...
Structure of N2O is similar to that of CO2 .
A. True
B. False
Solution
Structures of simple molecules can be deduced by using some simple rules given by Lewis.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the electronic theory of chemical bonding was given by Kössel and Lewis and it is also known as octet rule for according to this theory atoms combine to complete their octet in valence shell. Furthermore, covalent bonding was explained on the similar lines as formation of bond by sharing of valence electrons. To explain this Lewis dot structures were used in which valence electrons are represented by dots.
We can write the Lewis structure for a given molecule by following some simple steps as follows:
Let’s take a simple example of an oxygen molecule which has the formula O2 .
Firstly, we would calculate the total number of valence electrons contributed by all the constituting atoms. So, in molecule O2, each oxygen atom would contribute its six valence electrons giving a total of twelve electrons for the Lewis structure.
If there is a charge as well, we would incorporate that as well. In molecules, there is no charge.
Now we would write the skeletal structure of the molecule by using the symbols of the atoms and single bonds.
Lastly, remaining electrons would be used for multiple bonding or taken as lone pairs.
Let’s write the Lewis structure for N2O by using the above steps. In N2O, we can calculate the total valence electrons as follows:
\begin{array}{c}
{N_2}O = \left\\{ {2 \times \left( 5 \right)} \right\\} + 6\\\
= 10 + 6\\\
= 16
\end{array}
Now, we can write the skeletal structure of N2O as follows:
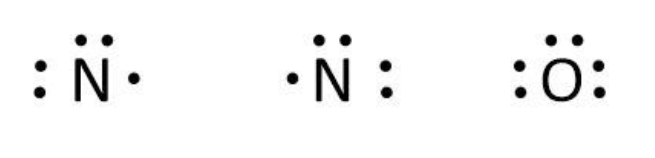
We can use the valence electrons for bonding and remaining as lone pairs as follows:
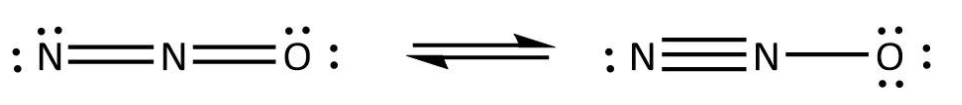
Similarly, we write the Lewis structure for CO2 by using the same steps. In CO2, we can calculate the total valence electrons as follows:
\begin{array}{c}
C{O_2} = 4 + \left\\{ {2 \times \left( 6 \right)} \right\\}\\\
= 4 + 12\\\
= 16
\end{array}
Now, we can write the skeletal structure of CO2 as follows:
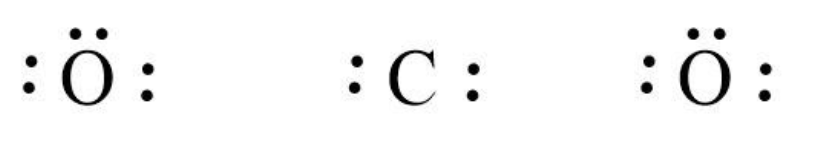
We can use the valence electrons for bonding and remaining as lone pairs as follows:
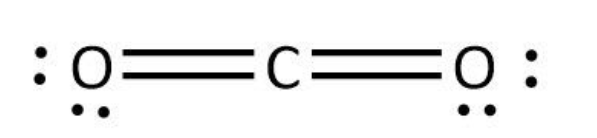
So, we can see that both the structures are linear. Hence, the given statement is true.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note:
We need to calculate the valence electrons carefully and distribute them as per the valency of the atom.
