Question
Question: Statement 1: Normal butyl alcohol and 2-butanol are isomers. Statement 2: Isomers vary in the numb...
Statement 1: Normal butyl alcohol and 2-butanol are isomers.
Statement 2: Isomers vary in the number of neutrons in the nucleus of the atom.
A) Both statement 1 and statement 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of Statement 1
B) Both statement 1 and statement 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of Statement 1
C) Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is not correct
D) Statement 1 is not correct but statement 2 is correct
E) Both statement 1 and statement 2 are not correct
Solution
To answer this question you must know the concept of isomerism and the different types of isomerism, that is structural and stereoisomerism. Isomers are molecules with identical formulas, but a distinct arrangement of the atoms in space.
Complete step by step solution:
The structure of n-butanol can be drawn as:
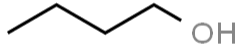
The structure of 2-butanol can be drawn as:
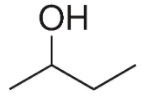
We know that isomers are defined as the molecules with the same molecular formula but possess a different arrangement of the atoms in space or different connectivity of atoms. Broadly isomers can be structural or stereoisomers. The phenomenon in which the molecules that form the isomers are connected differently is known as structural isomerism. The phenomenon in which the connectivity of atoms is the same in isomers but a different spatial arrangement is a stereoisomerism.
As in normal butyl alcohol and 2-butanol, the functional groups and the atoms in the molecules of these isomers are linked in different ways, they display the phenomenon of structural isomerism.
The atoms in which the number of neutrons are different are known as isotopes.
Thus, statement 2 is incorrect.
Hence, Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is not the correct statement.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
Geometric isomerism is one of the forms of stereoisomerism. The key point in geometrical isomers is the restricted rotation of a bond present somewhere in a molecule. At the most basic level of organic chemistry, carbon-carbon double bond is one of the examples leading to a restricted rotation. For example, 2-Butene can exist as cis and trans isomers because of the double bond that leads to the restricted rotation. This results in two isomers where the cis-isomer formed have the two methyl groups on the same side and the trans-isomer formed has the two methyl groups on opposite sides. 2-methyl propene and 2-methyl-2-butene contain a double bond but the groups attached to one of the C of the double bond are the same.
