Question
Question: State whether true or false: Electric charges leak rapidly through pointed edges of a conductor. ...
State whether true or false:
Electric charges leak rapidly through pointed edges of a conductor.
A. True
B. False
Solution
The answer to this question lies in the action of points associated with a charged body. On a perfectly round object, the charge spreads evenly but as the charged bodies become less symmetrical, the charge accumulation starts at various points.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a sphere and a triangle (shown here).
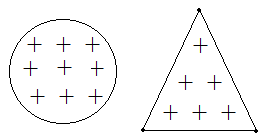
If we give charge to a sphere, it will spread evenly on the surface of the sphere, without any preference to a particular direction (unless the material has some flaws). When we take a triangle of the same material and we give it the same amount of charge, the charge tends to leak out through its pointed edges.
The amount of charge present at a point is inversely proportional to the radius of curvature. In the case of the sphere, the curvature was lesser as compared to the pointed edges of the triangle. Therefore, as more charge is accumulated at the edges it is able to leak as the air molecules near the edges interact with it. The charge leakage is fairly rapid because potential is fairly high enough at the points to cause ionization of the air molecules.
Therefore, it is a true fact that electric charges leak rapidly through air.
Note:
The radius of curvature is more for an object that only slightly seems to bend like a sphere whereas the radius of curvature is less when the bending is too sharp like the edges. The working of the Vande graaff generator is primarily based on the phenomenon of action of points so one can remember the result because of that.
