Question
Question: State True or False. \[\pi \] bond is formed by the colateral overlapping of atomic orbitals. A. ...
State True or False. π bond is formed by the colateral overlapping of atomic orbitals.
A. True
B. False
Solution
An orbital overlap is the concentration of orbitals on adjacent atoms in the same region. Orbital overlap can lead to bond formation. The extent of overlap depends on the two participating atoms, size and the valence electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
When Lateral overlapping or sideways overlapping of two atoms takes place, then it is known as a collateral overlap of their p orbital and the bond formed is known as covalent pi bond.
Further,
The collateral overlapping of orbitals form π bonds.
The collateral overlap of P orbitals leads to the formation of π bonds. These are covalent chemical bonds where two lobes of an orbital on one atom overlap two lobes of an orbital on another atom and there occurs a lateral overlapping. Each of these atomic orbitals has zero electron density at a shared nodal plane, passing through the two bonded nuclei.
On the other hand, S orbital will always overlap axially with any other orbital due to its symmetric structure; it will always form a sigma bond. The diagram of π bonds and sigma bond shown below.
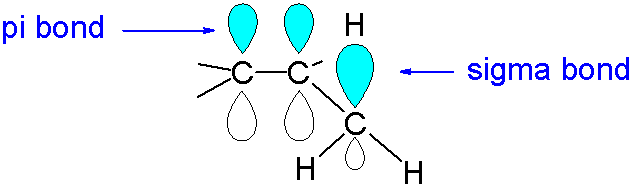
So, the given statement is true. The correct option is A.
Additional information:
On property of double bonds or pi – bonds that we must know is that they exist in the form of the shape of p – orbitals. P – orbitals have the shape of a two- lobe structure that expands over a given axis. Hence, these bonds have three dimensional geometries. Also, when it comes to lone pairs, these electrons always exist outside the lattice of the bond formation. Hence, existence of a lone pair, makes the over geometry of a relatively flat molecule into a 3 – dimensional structure.
Note: The ionic bond is an electrostatic attraction force between the ions. Coulomb’s law is extremely important in chemistry and physics because it describes the force between parts of an atom and between atoms, ions, molecules, and parts of molecules. As the distance between the charged particles or ions increases, the force of attraction or repulsion between them decreases and the formation of an ionic bond becomes less favorable. When charged particles move closer to each other, energy increases and ionic bonding is more favorable.
