Question
Question: State the working principle of Potentiometer. Explain with the help of circuit diagram, how the pote...
State the working principle of Potentiometer. Explain with the help of circuit diagram, how the potentiometer is used to determine the internal resistance of the given primary cell. In a potentiometer arrangement, a cell of emf 1.25V gives a balance point at 35cm length of the wire. If the cell is replaced by another cell and the balance point shifts to 63cm, what is the EMF of the second cell?
Solution
Potentiometer is a three-terminal resistor, which produces a voltage divider, through sliding or rolling contact. r=R(l2l1−1) and E=AρLI=KL, we can solve the question.
Formula used: r=R(l2l1−1) and, E=AρLI=KL
Complete step-by-step answer:
Potentiometer is a three-terminal resistor, which produces a voltage divider, through sliding or rolling contact. It works on the principle that potential across the wire depends on the length of the wire, which has uniform cross-sectional area and constant current flowing through it. It can be used to measure the internal resistance of the primary cell.
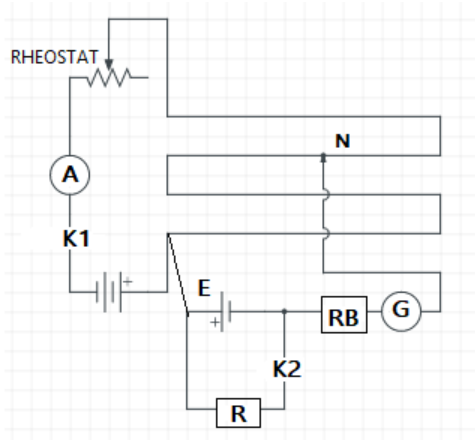
Connections are made as given in the diagram.
We know, V=IR Ohm’s law. Where I is current in the circuit, R is the total resistance and V is the voltage drop.
Also R=AρL. Where ρ is the resistivity, A is the area of cross-section of the wire, L is the length of the wire.
For any potentiometer ρ,A are constant.
Then, according to the principle, E=AρLI=KL, where E is the emf of the cell and K is the potential gradient.
Here E is the emf of the primary cell, and r is its internal resistance. To find r, plug inK2 the resistance box R, the potentiometer is balanced at say l1,
ThenE=Kl1=I(R+r).
When the plug out the K2, when the potentiometer is balanced at say l2, thenV=Kl2=IR
VE=Kl2Kl1=IRI(R+r)
l2l1=R(R+r)
Thus r=R(l2l1−1)
Using the given, emf of cell= E1=1.25V,l1=35cm and E2=E,l2=63cm
E2E1=l2l1
E1.25=6335
E=3563×1.25=2.25V
Hence the emf of the unknown is 2.25 V.
Note: Clearly understand the difference between what happens when K2 is plugged in and out. Try to remember the formula used. Remember the circuit diagram and the principle. Observe that the equations are interrelated, in terms of the potential.
