Question
Question: State tangent law in magnetism....
State tangent law in magnetism.
Solution
Tangent law is used to determine the strength of two perpendicular magnetic fields. This law is called tangent law because of the tangent factor in the expression. A torque will act on a magnet when it is placed in a magnetic field.
Complete step-by-step answer:
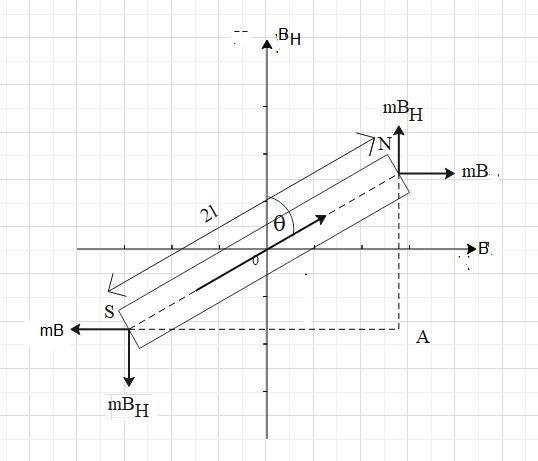
It states that when a magnet is suspended under the action of uniform magnetic fields B perpendicular to the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field ,BH, then the magnet comes to rest at an angle θ with respect to the field BH such that B=BHtanθ.
Let us suppose a bar magnet suspended in two mutually perpendicular uniform magnetic fields. The magnetic dipole moment M is given as
M=2l×m
Where 2l is the length of magnetic and m is the strength of each pole of the magnet.
When this magnet is placed in the magnetic field a torque acts on the magnet. Thus, when it is placed in a superposition of two magnetic fields then two torques act on the magnet and therefore, the magnet will rotate until it comes in an equilibrium position. At an equilibrium position, two couples balance each other.
Let us draw NA parallel to BH and SA parallel to B.
The torque acting on magnet due to field BH is given as
τ1=mBH×SA
The torque acting on magnet due to field B is given as
τ2=mB×NA
The torque τ1 rotates the magnet in an anticlockwise direction and τ2 rotates the magnet in the clockwise direction.
At equilibrium,
