Question
Question: State magnetic properties of \({O_2}\) and \({N_2}.\)...
State magnetic properties of O2 and N2.
Solution
Magnetic property of molecule explains on the basis of molecular orbital theory that, there or two types of molecule i.e., diamagnetic and paramagnetic when atomic orbital contains unpaired electron, it is paramagnetic and if it contains paired electrons the molecule is diamagnetic.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us explain the formation of bonds on the basis of molecular orbital theory.
Nitrogen molecule [N2]:
Electronic configuration of N-atom, 1s22s22px12py12pz1.
Total number of electrons present in N2-molecules is 14,7from each N-atom.
Atomic orbitals of N-atoms form two types of orbitals i.e., bonding and antibonding.
Bonding molecular orbitals form the additive effect of atomic orbitals and antibonding forms subtractive effect of atomic orbital.
Atomic orbitals and relative energies of them are shown in figure.
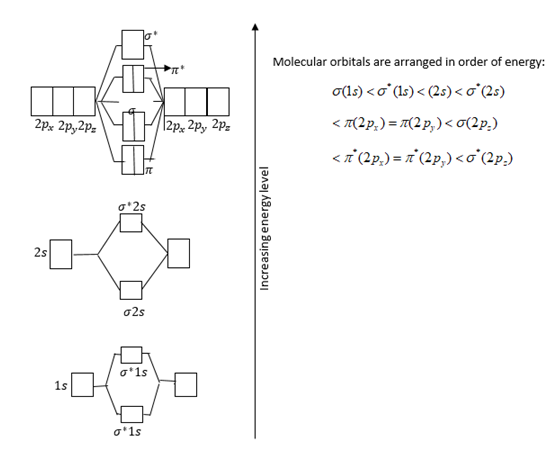
Total electrons filled in orbitals are as follows:
σ(1s)2σ∗(1s)2σ(2s)2σ∗(2s)2π(2px)2π(2py)2σ(2pz)2
Presence of no unpaired electron indicates that N2molecule is diamagnetic in nature.
Bond order of N2molecule is three, which means that N2molecule contains triple bonds.
Bond order=2Nb−Na
=28−2
Therefore, Bond order =3.
Nb= Bonding electron
Na= Antibonding electron
Formation of O2 molecule:
Electronic configuration of O-atom is, 1s22s22px22py12pz1.
Total number of electrons in the O2 molecule is 16. 8 from each O-atom.
14 electrons fill the atomic orbital as has been done in case of N2molecule.
The next orbital according to increasing energy π∗(2py)π∗(2pz)which have equal energy.
Two more electrons added according to Hund’s Rule.
Therefore, each orbital has one electron.
σ(1s)2σ∗(1s)2σ(2s)2σ∗(2s)2σ(2pz)2π(2px)2π(2py)2π∗(2px)1π∗(2py)1
Since πantibonding orbitals have one electron each i.e., unpaired electron.
Therefore, oxygen molecules are paramagnetic in nature.
Therefore, Bond order of O2molecule=2Nb−Na
=28−4
Therefore, Bond order =2.
Therefore, oxygen molecules form double bonds between O-atoms.
Therefore, from the above explanation, the correct option is B
Note: According to molecular orbital theory. Atomic orbitals of combining atoms lose their individual identity. Paramagnetic nature of oxygen and no-existence of He2,Ne2 molecule explained only by molecular orbital theory.
