Question
Question: Starting from glycol, how dioxane is obtained?...
Starting from glycol, how dioxane is obtained?
Solution
Glycol or ethylene glycol is an organic compound with the formula(CH2OH)2 . It is mainly used for two purposes, as a raw material in the manufacture of polyester fibers and for antifreeze formulations. It is an odorless, colorless, sweet-tasting, viscous liquid.
Complete step by step answer:
Dioxane is produced by the acid-catalysed dehydration of diethylene glycol, which in turn is obtained from the hydrolysis of ethylene oxide. The reaction can be represented from the following balanced chemical equation:
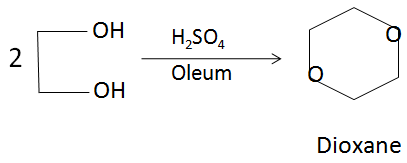
In the above reaction, the sulfuric acid acts as a dehydrating agent and produces a protonated solution in which the reaction takes place. There is a loss of water molecules in order to form the closed ring dioxane structure.
Minor uses of ethylene glycol include the manufacture of capacitors, as a chemical intermediate in the manufacture of 1,4-dioxane, as an additive to prevent corrosion in liquid cooling systems for personal computers, and inside the lens devices of cathode-ray tube type of rear projection televisions. Ethylene glycol is also used in the manufacture of some vaccines, but it is not itself present in these injections.
Note:
1,4-Dioxane is a heterocyclic organic compound, classified as an ether. It is a colorless liquid with a faint sweet odor similar to that of diethyl ether. The compound is often called simply dioxane because the other dioxane isomers (1,2−and1,3−) are rarely encountered. Dioxane is used as a solvent for a variety of practical applications as well as in the laboratory, and also as a stabilizer for the transport of chlorinated hydrocarbons in aluminum containers.
