Question
Question: Spermatids are formed after the second meiotic division from secondary spermatocytes. The ploidy of ...
Spermatids are formed after the second meiotic division from secondary spermatocytes. The ploidy of the secondary spermatocytes is
(a) n
(b) 2n
(c) 3n
(d) 4n
Solution
Meiosis (meiosis-I) is a reduction division that reduces the number of chromosomes into half and converts diploid cells into haploid. meiosis-II is the same as mitosis. Secondary spermatocytes that are haploid undergo meiosis-II.
Complete answer:
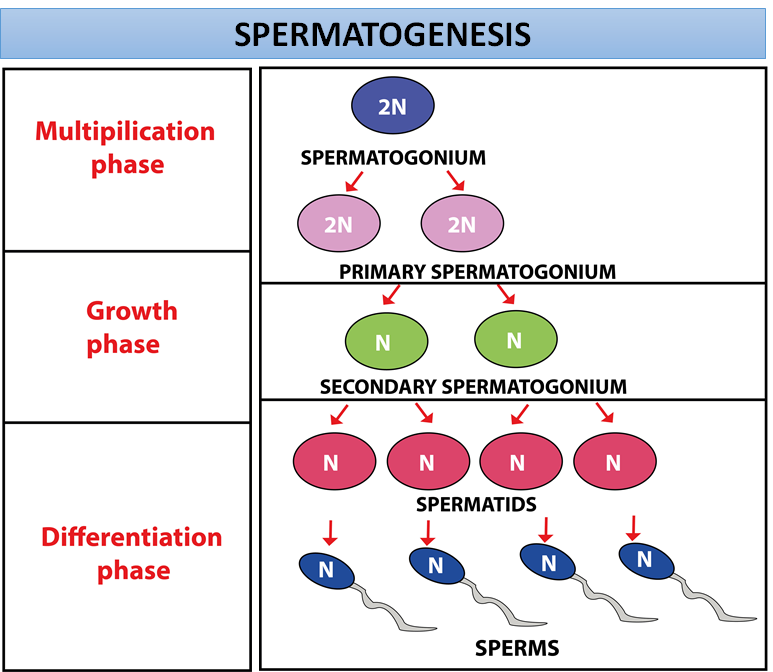
Each spermatogonial cell of humans is diploid and contains 46 chromosomes. Diploid spermatogonial cells develop into primary spermatogonial cells that undergo meiosis-I leading to the formation of haploid secondary spermatocytes. They undergo meiosis-II and produce spermatids that are haploid.
Additional Information:
- The process of formation of male germ cells called spermatids is called spermatogenesis.
- Spermatogenesis begins at puberty due to an increase in the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone(GnRH).
- The spermatogonial cells present in the seminiferous tubules multiply by mitotic divisions and increase in number.
- 23 pairs of chromosomes are present in the spermatogonial stem cell.
- Spermatogonial stem cells develop into primary spermatocytes.
- Primary spermatocytes undergo meiosis-I leading to the formation of secondary spermatocytes. In meiosis-I, the chromosome number will be reduced to half of the preceding cell. Here primary spermatocytes are diploid cells with 46 chromosomes, after meiosis-I, they turned into haploid cells with 23 chromosomes.
- The haploid secondary spermatogonial undergoes meiosis-II to produce four equal-sized haploid spermatids.
- By the process of spermiogenesis these spermatids get converted into sperms.
- Release of sperms from the seminiferous tubules whose heads are embedded in the Sertoli cells is released out by the process called spermiation.
So, the correct answer is ‘n’
Note: -The increased levels of GnRH act on the pituitary gland which stimulates the release of two hormones namely luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating (FSH) hormone.
-LH acts on the interstitial cells of Leydig and stimulates the secretion of androgens which in turn stimulates the process of spermatogenesis. FSH acts on Sertoli cells that release some factors that help in spermatogenesis.