Question
Question: Some equipment and materials are given. \[ZnS{O_4}\] solution, \[CuS{O_4}\] solution, \[Zn\] rod, ...
Some equipment and materials are given.
ZnSO4 solution, CuSO4 solution, Zn rod, Cu rod, Voltmeter, KCl solution, filter paper.
(a) Draw the diagram of the electrochemical cell which can be constructed using these equipment and materials and label the pans.
(b) Write equations of chemical reactions taking place in the two electrodes of this cell.
(Hint: reactivityZn>Cu)
Solution
Electrochemical cell is a cell or a device in which electrochemical reaction takes place. The transfer of electrons during a chemical reaction is called electrochemical reaction. Here conversion of one form of energy into another form occurs like chemical potential energy to electrical potential energy, or electrical potential energy to chemical potential energy.
Complete step by step answer:
Before understanding the diagram we have to be aware of a few things used in electrochemical cells.
Electrode: An electrode can be defined as an electrical conductor which connects the ions or electrochemical species present in solution with the external electrical circuit of the cell. Here Zn and Cu are the electrodes.
Electrolyte: An electrolyte can be defined as a solution containing free ions which acts as a conductor of charges in solution. Here ZnSO4 and CuSO4 are the electrolytes.
Salt bridge: A salt bridge is a tube which contains electrolytic solution and acts as a connection between two solutions. It is used to maintain the electrical neutrality between the electrolytes present in two different parts of the solutions. Here KCl is the salt bridge.
(a)
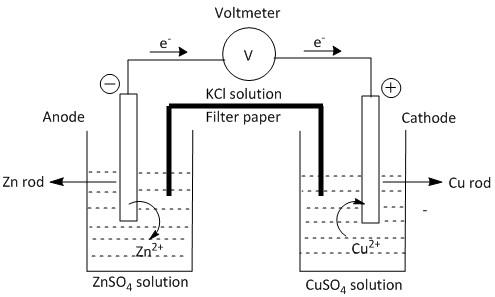
(b) Anode is defined as the electrode where oxidation takes place. Oxidation is the loss of electrons.
Cathode is the electrode where reduction takes place. Reduction is gain of electrons.
When Zn rod is dipped in ZnSO4 solution Zn2+ ion goes to the solution due to the oxidation process. When Cu rod is dipped in theCuSO4 solution, Cu2+ ion deposits on the metal surface from the solution due to the reduction process. This is because Cu2+ ion has greater attraction towards electrons than the Zn2+ ion. Thus the equation of the chemical reactions in the two electrodes can be written as:
At anode: Zn(s)→Zn2+(sol)+2e− (oxidation)
At cathode: Cu2+(sol)+2e−→Cu(s) (reduction).
Note: These cells are also known as galvanic cells. These are composed of two half cells. The electric energy or current will flow in the opposite direction to the flow of electrons. The concentration of electrons is more at anode than at cathode.
