Question
Question: Sketch the graph \(y=\left| x-5 \right|\). Evaluate \(\int\limits_{0}^{1}{\left| x-5 \right|dx}\). W...
Sketch the graph y=∣x−5∣. Evaluate 0∫1∣x−5∣dx. What does this value of the integral represent on the graph?
Solution
We explain the term absolute value of a number. How the modulus function always remains positive. We expand the function and break it into two parts. We also try to find the domain and the change of the graph at the particular point of x=5.
Complete step by step answer:
Modulus function f(x)=∣x∣ works as the distance of the number from 0. The number can be both positive and negative but the distance of that number will always be positive. Distance can never be negative.
In mathematical notation we express it with modulus value. Let a number be x whose sign is not mentioned. The absolute value of that number will be ∣x∣. We can say ∣x∣≥0.
We can express the function f(x)=∣x∣ as f\left( x \right)=\left\\{ \begin{aligned}
& x & \left( x\ge 0 \right) \\\
& -x & \left( x<0 \right) \\\
\end{aligned} \right..
We can write y=∣x−5∣ depending on the change of the graph.
So, y=\left\\{ \begin{aligned}
& x-5 & \left( x\ge 5 \right) \\\
& 5-x & \left( x<5 \right) \\\
\end{aligned} \right.
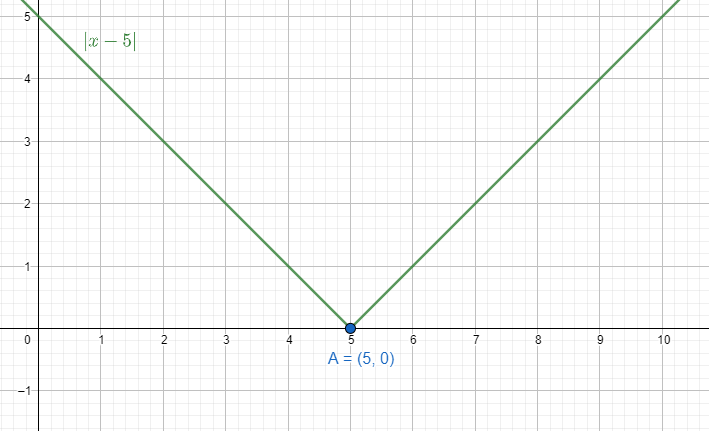
We can see in the domain of [0,1] for 0∫1∣x−5∣dx, the equation becomes y=5−x.
Therefore, 0∫1∣x−5∣dx=0∫1(5−x)dx. We use the formula of ∫xndx=n+1xn+1.
Therefore, 0∫1∣x−5∣dx=[5x−2x2]01=5−21=29.
This value indicates the area under the line y=5−x in the region bounded by lines y=0, x=0 and x=1.
Note: The only time the absolute value becomes 0 is when the number itself is 0. For any other number the absolute value is greater than 0. Therefore, we can say ∣x∣>0 when x=0. In our given function y=∣x−5∣ the absolute value reaches at 5.
