Question
Question: Sketch and label the figure of the following plant and explain briefly its characteristics. _Funar...
Sketch and label the figure of the following plant and explain briefly its characteristics.
Funaria
Solution
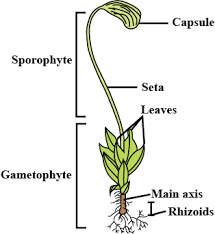
In Funaria , the sporophyte is semi-parasitic. It has three distinct parts—foot, seta, and capsule. These are seen in the mature sporophyte after its differentiation. The plant body is a gametophyte which is leafy. It consists of the stem. It is covered with small and simple leaves. The stem is branched (branching is monopodial). A branch may originate below the leaf.
Complete answer:
Under the division Bryophyta of kingdom Plantae, the genus Funaria represents the moss plants.
It has a gametophytic plant body with slender and erect gametophores.
Branched, filamentous and multicellular rhizoids (tuft-like) can be seen originating from the base of the stem. These possess oblique septa. They may become brown in color on maturity. They help in absorption and fixation and may develop chlorophyll (only when they are present on an exposed axis).
Sessile and ovate leaves in the form of apical tufts are arranged on the axis spirally showing a phyllotaxy of . These leaves have acute apices (with each leaf having the entire margin) and contain mid ribs. There are Three types of leaves:
Scaly leaves – small, membranous and present on the lower part of the gametophores
Foliage leaves – bigger, green leaves present in the middle
Perichaetial leaves – compactly arranged at the upper portion
The sporophyte which is borne on the gametophyte is divided into:
Foot – it is embedded in the gametophyte.
Seta – it’s the elongated stalk; capsule found at its tips.
Capsule – haploid spores are present (sexual reproduction leads to formation of haploid spores in Funaria).
Note:
Funaria undergoes vegetative reproduction by fragmentation of primary protonema, formation of - secondary protonema from any part of the gametophyte, formation of gemmae on terminal cells of the protonema, development of bulbils on the rhizoids. Funaria is monoecious. Antheridium is the male sex organ which is enclosed by perigonial leaves. A large number of long multicellular hair called paraphysis is seen. They help in photosynthesis as they contain chloroplast. Archegonium is the female sex organ and is surrounded by perichaetial leaves. Paraphyses are also seen here. The antherozoids reach the archegonium by chemotaxis.
