Question
Question: Simplify: \[\dfrac{{{{\sin }^3}\theta + {{\cos }^3}\theta }}{{\sin \theta + \cos \theta }} + \sin...
Simplify:
sinθ+cosθsin3θ+cos3θ+sinθcosθ
Solution
Here we will use the formula of (a3+b3)=(a+b)(a2+b2−ab), a and b are two different values. We will simplify using this formula to simplify the given trigonometric equation.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Step 1: By comparing the given term sin3θ+cos3θ with the formula (a3+b3)=(a+b)(a2+b2−ab), we can write it as below:
⇒(sin3θ+cos3θ)=(sinθ+cosθ)(sin2θ+cos2θ−sinθcosθ)
By substituting this value in this given expression sinθ+cosθsin3θ+cos3θ+sinθcosθ , we get:
⇒sinθ+cosθ(sinθ+cosθ)(sin2θ+cos2θ−sinθcosθ)+sinθcosθ ……………………… (1)
Step 2: By dividing the term sinθ+cosθ from the numerator and denominator side, we get:
⇒(sin2θ+cos2θ−sinθcosθ)+sinθcosθ
By eliminating the term sinθcosθ from the above expression (sin2θ+cos2θ−sinθcosθ)+sinθcosθ, we get:
⇒sin2θ+cos2θ
Step 3: As we know the value of sin2θ+cos2θ=1, so the answer will be equal to 1.
∴sinθ+cosθsin3θ+cos3θ+sinθcosθ=1
Note: Students need to remember the basic formulas for solving these types of questions. Some of them are mentioned below:
(a+b)2=(a2+b2+2ab)
(a−b)2=(a2+b2−2ab)
(a+b)3=a3+b3+3ab(a+b)
(a−b)3=a3−b3−3ab(a−b)
(a3+b3)=(a+b)(a2+b2−ab)
(a3+b3)=(a−b)(a2+b2+ab)
Also, students need to remember that the value of sin2θ+cos2θ=1 , proof of which as shown below for your better understanding:
Assume that in a triangle, there are three sides of length x, yand z as shown in the below figure:
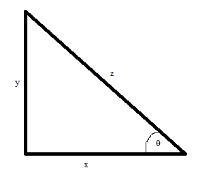
As we know
sinθ=zy , i.e. the Opposite side is divided by the hypotenuses. And the cosθ=zx, i.e. base divided by the hypotenuses.
By using the Pythagoras theorem, we get:
z2=x2+y2 i.e. (Hypotenuse)2=(Base)2+(height)2
Also,
sin2θ+cos2θ=(zy)2+(zx)2, by taking z common from the denominator part and adding the numerator one we get:
