Question
Question: Shown below is an experimental set up with a semiconductor diode (i) Identify the experiment (ii...
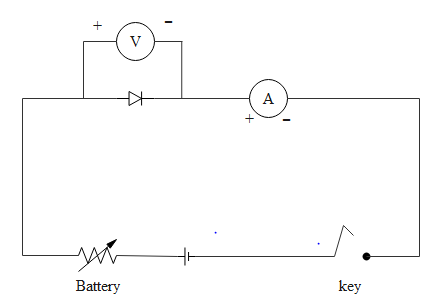
Shown below is an experimental set up with a semiconductor diode
(i) Identify the experiment
(ii) Draw the resulting graph
Solution
If we combine two extrinsic semiconductors we get diodes. Extrinsic semiconductor in which electrons are excess are called n-type semiconductor whereas extrinsic semiconductor in which holes are excess are called p-type semiconductor. They conduct electricity only in forward bias
Complete step by step answer:
Diodes are the combination of intrinsic semiconductors. By sandwiching the extrinsic semiconductors we get diodes. Now at the sandwiched region, charge carriers from the p- type semiconductor i.e holes will move to the n type side and that region gets the positive charge, while electrons from the n- type goes to the p- region and that ragion gains negative charge. Due to this positive and negative charges at the sandwiched region carries some voltage called barrier voltage.
If p type semiconductor is connected to a positive terminal of the battery then that is forward bias. It is clearly shown in the below diagram
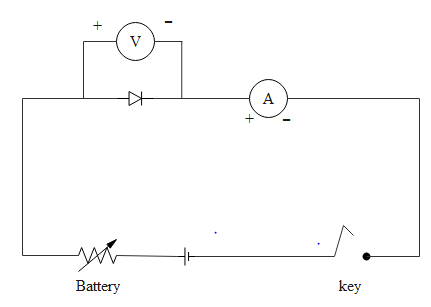
So this experiment indicates current flow through diodes only in forward bias.
The base end of the triangle type diode structure denotes the p-type semiconductor, while the sharp edge of the triangle denotes the n- type of the semiconductor. In the above diagram, it is clearly shown that p type is connected to positive terminal while n type to negative terminal.
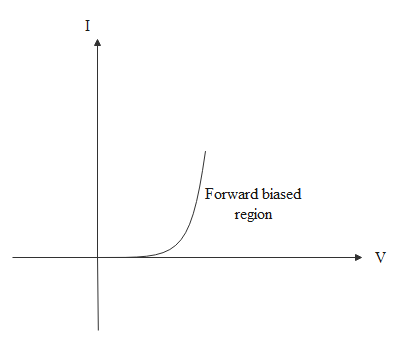
The plot of biased voltage and current for the forward bias will be
Note:
In the plot initially for some voltage difference, even though voltage difference increases the current will increase because that voltage difference is compensated by the barrier potential. Current increases only after the voltage difference overcomes the barrier potential. After that even for small increases in voltage, current increases much significantly.
