Question
Question: Select correct statement for \(Br{F_5}.\) (A) All fluorine atoms are in the same plane. (B) Four...
Select correct statement for BrF5.
(A) All fluorine atoms are in the same plane.
(B) Four fluorine atoms and Br atoms are in the same plane.
(C) Four fluorine atoms are in the same plane.
(D) It hasF−Br−Fbond angles at 90∘.
Solution
BrF5 is an interhalogen compound. When two different halogens form compounds among themselves, interhalogen compounds are formed. Such compound may have general formula XX1,XX31,XX51 and XX71. Here X is halogen of large size and X1of small size and X is more negative.
Complete step by step answer:
In BrF5Bromine is the central atom and fluorine atoms present around it.
The name of the compound is Bromine pentafluoride.
Bromine atoms have larger size than fluorine and fluorine is more electronegative.
Electronic configuration of Br, 1s22s22p62s23p63d104s24px24py24pz1
Ground state configuration =
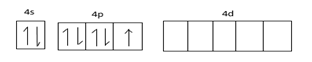
Excited state configuration =
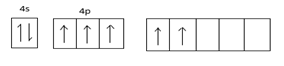
Hybridized state =
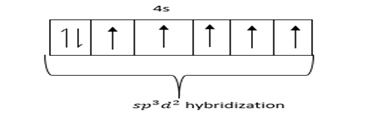
Geometry of BrF5 is square pyramidal and hybridization sp3d2.
In sp3d2, 4 Fluorine atoms and one Br-atom present in the same plane.
Bond angle between them is 90 Degrees.
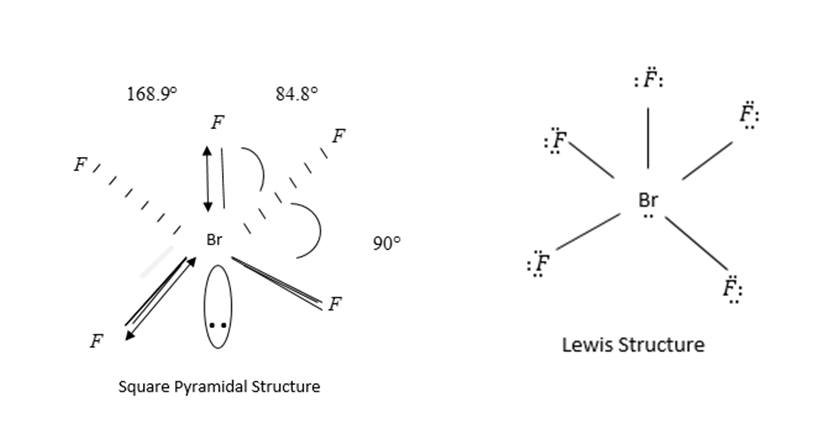
In Lewis structure we see that octets of each element should be complete. On fluorine atoms 3 lone pairs of electrons and on bromine atom only one lone pair is present.
By VSEPR theory 4 bond pairs occupy corners of squares and one bond pair and lone pair of electrons occupy equatorial position to minimize repulsion between lone pair and bond pair of electron.
Interhalogen compounds are covalent in nature due to low electronegativity difference between halogens. They are diamagnetic in nature. They are more reactive than halogen.
Interhalogen compounds behave as strong oxidizing agents and attack other elements to give a mixture of halides.
Therefore, the above explanation, the correct option is [D] Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Note: Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogen. This is because the X−X− bond present in them is weaker than X−X andX1−X bonds.
