Question
Question: Schottky defects lower the density of related solids. Why?...
Schottky defects lower the density of related solids. Why?
Solution
Any solid crystal of a compound is not perfect, means they consist of defects when crystallization occurs at a fast or moderate rate. Defects are the irregularities that arise in the arrangement of constituent particles in a lattice.
Complete answer:
Defects are the irregular arrangement of particles in a crystal lattice. They may arise due to defective crystallization, which makes up the molecule. As a result, many vacancies or voids or even impurities may take the places in the crystal lattice of a substance.
Defects can be of various types, one such is the point defect where the irregularity in arrangement is at one ideal point in the crystal. These defects give rise to stoichiometric defects that disturb the stoichiometry of the crystal.
Schottky defect is a type of stoichiometric defect. This defect occurs in ionic solids. It occurs in compounds where the size of anion and cation is almost similar. In this type of defect equal numbers of anions and cations are missing from the crystal lattice. As depicted in the following diagram,
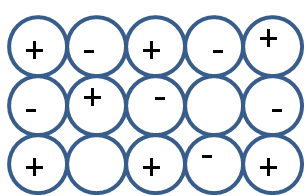
The equal number of missing anion and cation decreases the overall density. As density is mass upon volume, the missing ions decrease the mass, hence the density in schottky defects also decreases.
Note:
Schottky defects can be seen in the compounds like alkali -metal halides, where the cation and anion are of almost similar size. Some examples of compounds with this type of defects are NaCl, KCl, CsCl, and AgBr. The volume in these types of defects remains constant.
