Question
Question: S atom in \({\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_3}\) involves hybridization: A.\({\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\) B....
S atom in SO3 involves hybridization:
A.sp2
B. p2
C. sp
D. sp3
Solution
We will determine the geometry of the molecules by drawing the Lewis structures. Lewis structure is drawn by arranging the total valence electrons around central and surrounding atoms. The sum number of lone pairs at the central atom and the number of sigma bonds gives the type of hybridization.
Complete step-by-step solution: According to the valence bond theory, the orbitals of metals combine to form orbitals of the same energy. These orbitals are known as hybrid orbital. Each ligand donates an electron pair to a hybrid orbital.
We will write the Lewis structure as follows:
We will write the basic structure. Then decide the central atom around which we will write all atoms of the molecule. The least electronegative atom is the central atom.
Then we will count total valence electrons.
Two electrons are used in the formation of a bond.
We will count the total electron used in bond formation.
We will subtract the electrons used in bond formation from the total valence electrons.
Then we will arrange the remaining electrons around each atom to complete the octet.
Based on the number of electron pairs the hybridization and shape is determined.
| Number of electron pair around central atom | Hybridization |
|---|---|
| 2 | sp |
| 3 | sp2 |
| 4 | sp3 |
The Lewis structure of SO3is as follows:
Total valence electrons are as follows:
=(6×1)+(6×3)
=24
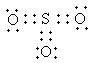
The number of sigma bonds of central atom sulphur is three so, the hybridization of SO3 issp2.
So, S atom in SO3 involves hybridization sp2.
Therefore, option (A) sp2, is correct.
Note: Valence electrons of sulphur and oxygen both are six. Pi bonds do not include in the counting of electron pairs around the central atom. The number of hybrid orbitals depends upon the number of sigma bonds. During counting the valence electrons, one is subtracted for each positive charge because a positive charge means an electron is lost. One is added for each negative charge because a negative charge means an electron is gained.
