Question
Question: Rocket works on the principle of conservation of: A. Mass B. Energy C. Momentum D. Velocity...
Rocket works on the principle of conservation of:
A. Mass
B. Energy
C. Momentum
D. Velocity
Solution
According to Newton’s Third Law, every action has an equal and opposite reaction, in a straight line. Here, in rocket propulsion, the thrust force is the reaction of the expulsion of exhaust gases. The expelled gases provide momentum for the rocket to accelerate in the opposite direction.
Formula used:
FT=vexdtdm
Complete answer:
Let us draw a free body diagram of a rocket to understand better.
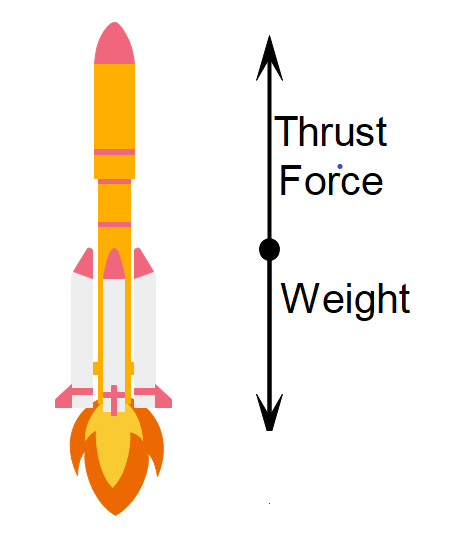
From Newton’s 3rd law, the action here is the expulsion of gases through the rear end of the rocket. This expulsion gives rise to thrust force.
This thrust force helps the rocket to overcome its weight.
From, Newton’s second law force is the rate of change of momentum. So thrust force is given by
FT=dtdp=dxd(mvex)=vexdtdm
Here,
FT is the thrust force
p is the momentum of the rocket
m is the mass of the rocket
vex is the exhaust velocity.
Here, you must understand that the rocket is subject to change in mass due to the expulsion of burnt fuels as exhaust gases.
The escape of the gases through the tailpipe provides a large momentum to the rocket in the forward direction. And with the decrease in mass of the rocket, the acceleration keeps on increasing.
Simply put, the rocket gains momentum equivalent to the momentum of the gas expelled from the tailpipe. Yet, in the opposite direction, they keep expelling the gases, even after the rocket has started moving. And consequently, the rocket keeps on increasing its momentum, so as opposed to going at constant velocity due to the continuous decrease in the mass. So, momentum is conserved.
Hence, the rocket works on the principle of conservation of momentum.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
From the thrust force equation, you should understand that the mass of the rocket is subject to change. It is due to the release of exhaust gases. As the gases are released from fuel combustion, the mass of the rocket is changing with respect to time.
The acceleration of the rocket is given by
a=dmFT−W.
Where W is the weight of the rocket and dm is the mass of the rocket which is subject to change. Please note that acceleration only exists in a vertical direction.
