Question
Question: Refractive index for a material for the infrared light will be, A. equal to that of ultraviolet ra...
Refractive index for a material for the infrared light will be,
A. equal to that of ultraviolet rays.
B. less than for ultraviolet rays.
C. equal to that of red colour of light.
D. greater than the ultraviolet rays.
Solution
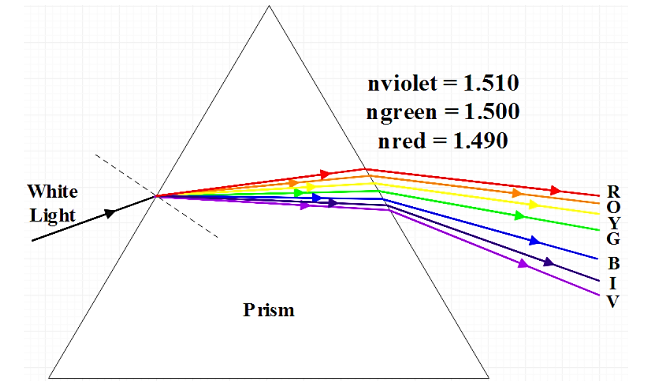
Refractive Index is calculated by taking the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to that of a specific medium. The wavelength of the ultraviolet is less than that of the infrared rays. This will help you in answering the question.
Complete step by step answer:
As we all know, the equation of refractive index is the ratio of the velocity of the light in vacuum to the velocity of the light in the medium. This can be written as,
μ=VC
Where C be the velocity of light in vacuum and it is a constant and V be the velocity of the light in specific mediums. And also we know that the velocity of light is the product of frequency and the wavelength of the light used. Therefore we can write that,
V=fλ
Where f be the frequency and λ be the wavelength of the light. Substituting this in the equation of refractive index,
μ=VC=fλC
From this we can say that,
⇒μ∝λ1
As we all know the wavelength of the ultraviolet is less than that of the infrared rays, the refractive index will be having the opposite relation. That is the refractive index of the ultraviolet will be higher than that of infrared rays.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The refractive index of an object changes with the wavelength or the frequency of the light. This phenomenon is known as dispersion. By this process, the prisms and rainbows separate white light into its constituent spectral colours. In regions of the spectrum where the substance will not absorb light, the refractive index is getting decreased with the increase in the wavelength, and thus the frequency gets increased. This is known as the "normal dispersion". This is in contrast to “anomalous dispersion". In this the refractive index increases with wavelength. The normal dispersion means that the refractive index is higher for blue light than for red for visible light.