Question
Question: Reduction of \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{NC}}\) with ...
Reduction of CH3CH2NC with hydrogen in presence of Ni or Pt as catalyst gives:
A.CH3CH2NH2
B.CH3CH2NHCH3
C.CH3CH2NHCH2CH3
D. (CH3)3N
Solution
We should know the structure of the isonitrile group and the reduction mechanism of isonitrile to answer this question. In isonitrile, nitrogen forms four bonds, so it has a positive charge and carbon has a negative change. It gets protonated. TheCH3CH2NC itself indicates the type of amine formed.
Complete step-by-step answer: The reduction of isonitrile with hydrogen in presence of Ni or Pt is known as catalytic hydrogenation. The −NC is known as isonitrile. The reduction of isonitrile with hydrogen in presence of Ni or Pt as a catalyst is shown as follows:
In isonitrile, the negative changed carbon work as a nucleophile. It attacks hydrogen and gets protonated. The triple bond shifts to the nitrogen and the lone pair of the nitrogen attacks on another hydrogen. Again the breaking of the N=C bond results in the secondary amine.
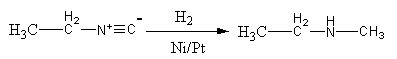
The reduction of isonitrile with hydrogen in presence of Ni or Pt gives secondary amine.
So, the reduction of CH3CH2NC with hydrogen in presence of Ni or Pt as catalyst gives CH3CH2NHCH3.
Therefore, option (B) CH3CH2NHCH3, is correct.
Note: The −NC is isonitrile. It is also known as isocyanide and −CN is known as nitrile. The reduction of isonitrile gives secondary amine. The reduction of nitrile gives the primary amine. The isonitrile can also be reduced by using strong reducing agents like lithium aluminium hydride LiAlH4 . The amine produced by the reduction has one carbon more than the reactant. The isonitrile test is used for the detection of primary amine. In this test, primary amine is treated with potassium hydroxide and trichloromethane. The isocyanide or isonitrile is formed as a product which has an unpleasant odour.
