Question
Question: Reduction of aldehydes and ketones into hydrocarbons using zinc amalgam and conc. \[HCl\] is called:...
Reduction of aldehydes and ketones into hydrocarbons using zinc amalgam and conc. HCl is called:
A. Clemmensen reduction
B. Cope reaction.
C. Dow reduction
D. Wolf-Kishner reduction
Solution
Reduction is a process of addition of hydrogen to a functional group. During the process metals are employed to carry out the reduction reaction which itself undergoes oxidation.
Complete step by step answer:
Aldehydes and ketones are an important class of organic compounds. They possess a variety of organic reactions in synthetic chemistry. They are together called carbonyl compounds. Both the aldehyde and ketone possess a C=O functional group. In aldehyde the C=O is attached to a hydrogen atom while in ketone the C=O is attached to an alkyl functional group.
In the several organic reactions of aldehydes and ketones, the most common are the oxidation and reduction reactions. The reaction involves the addition of hydrogen atoms from a hydride source. For these different methods are used. In this case the zinc metal and conc. HCl induced reduction is employed.
The reaction is
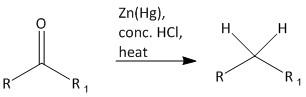
The reaction involves loss of oxygen atom with gain of two hydrogen atoms. The product obtained by the reduction of aldehyde and ketone is a hydrocarbon. The reaction is introduced by Clemmensen. The exact reaction condition is using zinc dust and anhydrous solution of hydrogen chloride (37% ) in presence of diethyl ether or acetic anhydride.
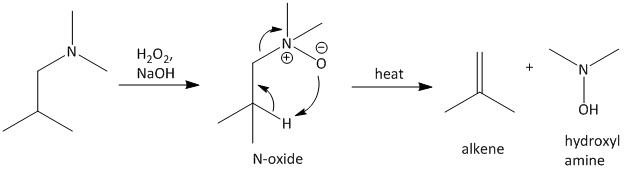
Cope reaction is an elimination reaction. Here an alkene is produced from an N-oxide. The side product of the reaction is a hydroxyl amine. The reaction involves a five membered transition state which undergoes rearrangement.
Dow's Process is hydrolysis of chlorobenzene for the generation preparation of phenol. It is an example of aromatic nucleophilic substitution. The reaction is performed by treating chlorobenzene with aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide at 350∘C and 300bar pressure to yield sodium phenoxide. This acidification produces the desired phenol.
Wolf-Kishner reduction is also a type of reduction of aldehyde and ketones. In this process the carbonyl compound is treated with hydrazine hydrate to generate the hydrazone. The hydrazone on reaction with base produces the desired alkane with release of nitrogen gas as side product.
Hence option A is the correct answer, i.e. reduction of aldehydes and ketones into hydrocarbon using zinc amalgam and conc. HCl is called Clemmensen reduction.
Note:
As strongly acidic conditions (37% HCl) are used in Clemmensen reduction so the substrate must be stable under this condition for the reaction to succeed. Wolff-Kishner reduction is an alternative used for acid-sensitive substrates.
