Question
Question: Reactions of deuterated bromocyclohexene, 1 and 2, by the E2 mechanism give mono deuterated cyclohex...
Reactions of deuterated bromocyclohexene, 1 and 2, by the E2 mechanism give mono deuterated cyclohexene A and d'deuterated cyclohexene B. Which of the statements (a)-(b) best indicates the most probable selectivities of two reactions.
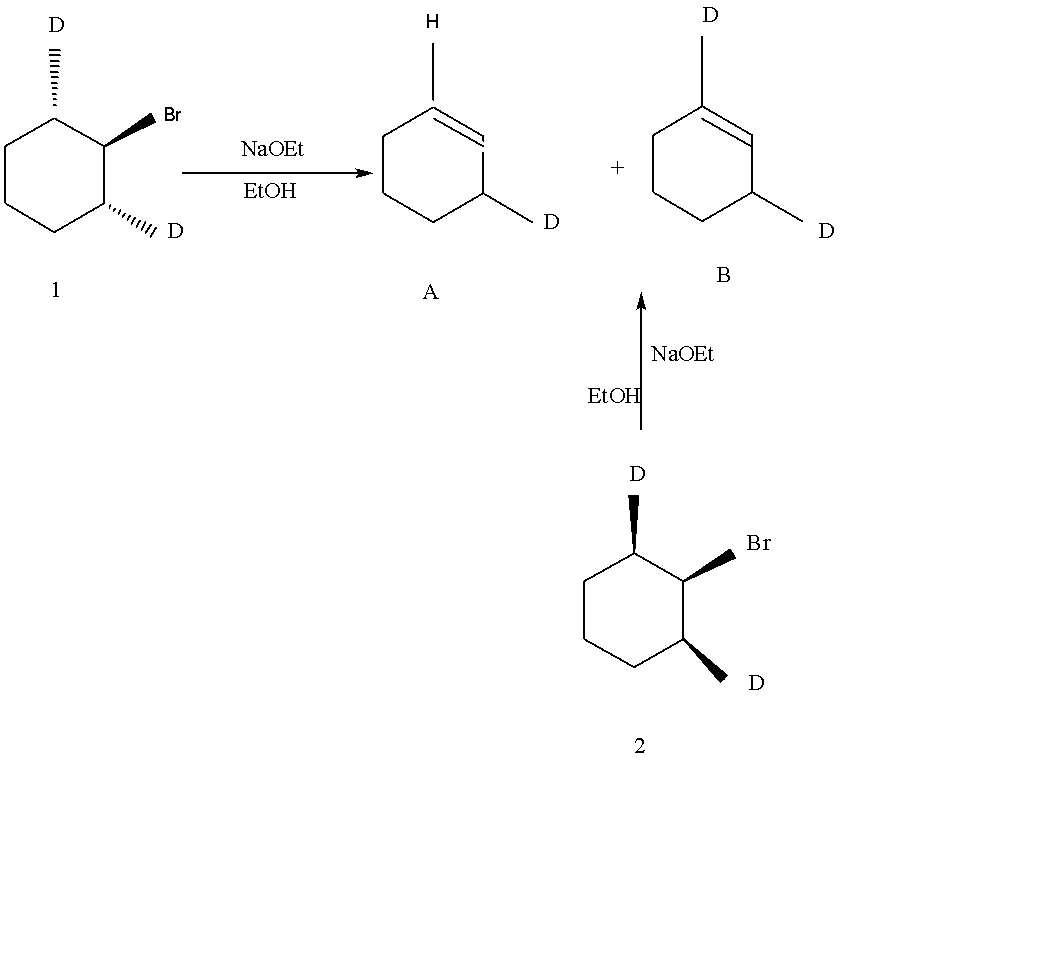
A.Product is A form both 1 and 2.
B.Product is B from both 1 and 2.
C.Product is A from 1 and B from 2.
D.Product is B from 1 and A from 2.
Solution
Elimination reactions can be very useful in organic synthesis for producing alkenes, alkynes and allenes on a preexisting scaffold. Synthetic issues associated with eliminations include the suppression of substitution and suitability in synthesis will be discussed and methods involving stereo selective and stereospecific transformation to di, tri, and tetra substituted alkenes will be disclosed. Elimination reactions that form alkynes and both enantioenriched and racemic allenes are also featured.
Complete answer:
Elimination reactions are commonly known by the kind of atoms or groups of atoms leaving the molecules. The removal of a hydrogen atom and halogen atom. E reaction occurs by elimination reaction and facilitated. When the H and nucleofuge on adjacent Carbon atoms can achieve an antiplanar. When the 1 with the Bromine axial, the trans C-D bonds are both axial and coplanar with the bromine. Elimination of D with Bromine gives yield A by the E2 mechanism. As it is, the conformation of 2 with the Br axial, two adjacent are in trans position. Here C-H bonds are in axial and coplanar with the Br and give yield B by the E2 mechanism.
So, Option C is the correct answer.
Note: E2 reactions are typically seen with secondary and tertiary alkyl halides, but a hindered base is necessary with a primary halide. The mechanism by which it occurs is a single step concerted reaction with one transition state. The rate at which this mechanism occurs is second order kinetics, and depends on both the base and alkyl halide.
