Question
Question: Reaction of a carbonyl compound with one of the following reagents involves nucleophilic addition fo...
Reaction of a carbonyl compound with one of the following reagents involves nucleophilic addition followed by elimination of water. The reagent is:
(A) Hydrocyanic acid
(B) Sodium hydrogen sulphite
(C) A Grignard reagent
(D) Hydrazine in presence of feebly acidic solution
Solution
The reagent forms imines as a final product which does nucleophilic attack on carbonyl carbon followed by the loss of water. The reagent has a nucleophilic nitrogen atom in its structure.
Complete step by step solution:
We will take a look at all the given reagents in order to find the answer.
- Hydrocyanic acid or HCN has cyanide ion as a nucleophile. It can attack the carbonyl group of carbon and form cyanohydrins. The cyanohydrins are stable enough that they do not lose a molecule of water. Thus, it is not the correct answer.
- Sodium hydrogen sulphite or NaHSO3 is an ionic compound and does not give any nucleophilic addition reaction with carbonyl groups.
- A Grignard reagent can attack the carbonyl group of the carbon via a nucleophile but the reaction does not involve loss of water molecule.
- When a carbonyl compound is allowed to react with hydrazine in a feebly acidic medium, the nucleophilic nitrogen atom attacks the electrophilic carbon atom of the carbonyl group. Then, Water molecule is lost in the presence of a weak acidic medium and an imine is formed as a final product. Here, a weak acidic medium helps the hydroxyl group to leave. The reaction can be shown as below.
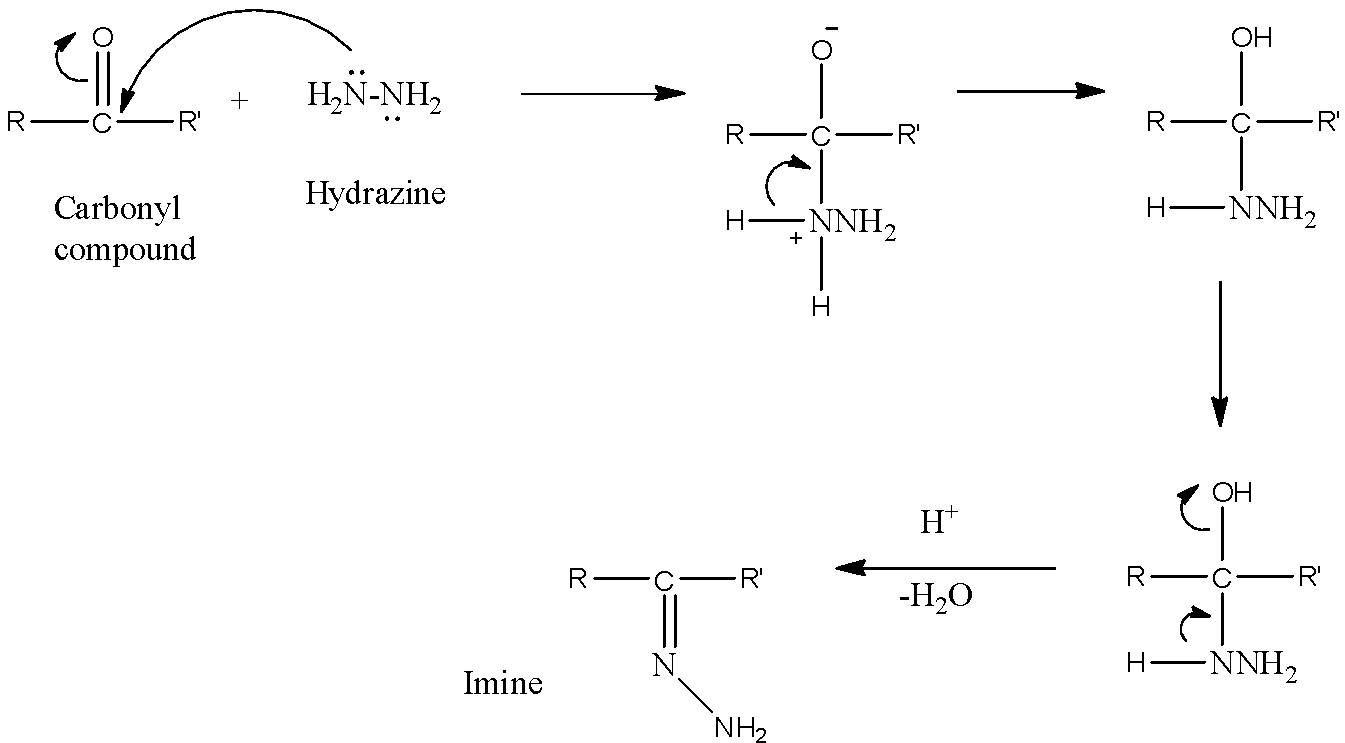
So, we can conclude that when a carbonyl compound reacts with hydrazine in a feebly acidic solution, then nucleophilic attack is involved and imine is formed.
Thus, we can say that the correct option is (D).
Note: Note that the α-hydroxy amines are not stable and so that they always form imines upon losing water molecules. Sodium hydrogen sulphite is a weak base and it only reacts with strongly acidic compounds.
