Question
Question: Reaction of 1,4 dibromobutane with Mg turnings in ether gives the bis Grignard’s reagent \(BrMgC{H_2...
Reaction of 1,4 dibromobutane with Mg turnings in ether gives the bis Grignard’s reagent BrMgCH2CH2CH2CH2MgBr. What is the reaction of meso-2,3 dibromobutane with Mg under the same condition.
A. Trans-2-butene
B. cis-2-butene
Solution
Meso compounds are superimposable on their mirror image and in spite of having two or more stereogenic centers, the molecule is not chiral. Meso compounds have multiple chiral centers. A compound having a total of n chiral centers cannot obtain the theoretical maximum of 2n stereoisomers if one of the stereoisomers is meso.
Complete answer:
Grignard Reagent has a generic formula R-Mg-X, R is an organic group and X is a halogen.
According to the question, bis-Grignard’s reagent is formed on a reaction of 1,4-dibomobutane with Mg turnings in ether.
BrCH2CH2CH2CH2BrMgDry etherBrMgCH2CH2CH2CH2MgBr
When meso-2,3-dibromobutane reacts with Mg one of the product formed is meso-CH3CH(MgBr)CH(MgBr)CH3 and the other product formed will be a Trans-2-butene.
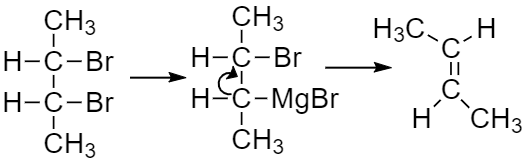
If the reaction takes place at one of the carbon then MgBr will act as Grignard reagent and the adjacent carbon will be a nucleophile and the reaction will take place as SN2 a reaction, the structure that has a better leaving group as one of its substituents and gives least steric hindrance to approaching nucleophile for it undergoes SN2 reaction at a faster rate.
The halogen will be removed and the product formed will be an alkene (Tran -2-butene in this case).
Therefore the correct answer is option B.
Note:
Cis-trans isomerism is configurational isomerism. The prefix “cis” is a Latin term which means “this side of” and the prefix “Trans” means “the other side of”.
The functional groups are on the same side of the carbon-carbon bond in the cis position but the functional groups are present on the opposite sides of the bond in Trans orientation. The cis isomer is usually polar but it may not be polar in Trans isomer because dipoles of opposite groups cancel each other.
