Question
Question: Rank the following alkenes in order of decreasing heats of hydrogenation: (largest first) 
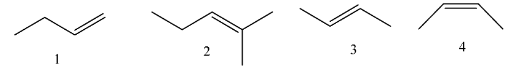
(A) 2 > 3 > 4 > 1
(B) 2 > 4 > 3 > 1
(C) 1 > 3 > 4 > 2
(D) 1 > 4 > 3 > 2
Solution
Heat of hydrogenation of an alkene is the standard enthalpy of catalytic hydrogenation of an alkene. Catalytic hydrogenation of an alkene is always exothermic. Therefore, the heat of hydrogenation of alkenes is always negative
Complete step by step solution:
We know that Heat of hydrogenation is related to stability of the alkenes.
If an alkene is very stable its heat of hydrogenation is very less.
If an alkene is less stable its heat of hydrogenation is more.
Stability of alkene means alkene won’t convert into alkane easily.
The stability of alkenes can be calculated using hyper conjugation.
Hyper conjugation is directly proportional to the number of alpha hydrogens.
The carbon which is adjacent to the double bond is called alpha carbons, and the hydrogens which are attached to alpha carbon are called alpha hydrogens.
As the number of alpha hydrogens are increasing the stability of the alkene increases that much, meaning less heat of hydrogenation.
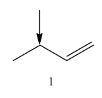
Coming to given options, molecule-1, the molecule has two alpha hydrogens.
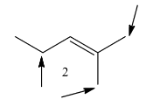
Coming to molecule-2, the molecule has eight alpha hydrogens.
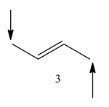
Coming to molecule-3, the molecule has six alpha hydrogens, sterically stable.
Coming to molecule-4, the molecule has six alpha hydrogens, sterically less stable.
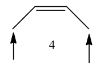
Stability of the given molecules is as follows.
2 > 3 > 4 >1
But according to the heat of hydrogenation the order is as follows.
1 > 4 > 3 > 2
So, the correct option is D.
Note: Stability of the molecule is going to depend on the number of alpha hydrogens and steric hindrance of the molecule. If steric hindrance is high, the molecule is less stable.
