Question
Question: Pure water freezes at 273 K and 1 bar. The addition of 34.5 g of ethanol to 500g of water changes th...
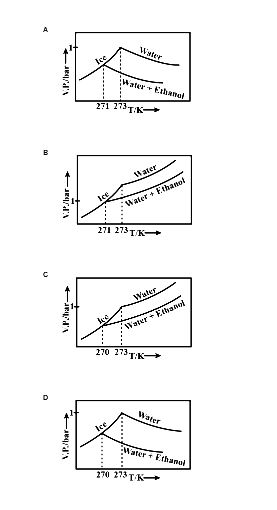
Pure water freezes at 273 K and 1 bar. The addition of 34.5 g of ethanol to 500g of water changes the freezing point of the solution. Use the freezing point depression constant of water as 2 K kg/mol. The figures shown below represent plots of vapour pressure (V.P). among the following, the option representing a change in the freezing point is:
Solution
The lowering of vapour pressure causes a lowering of the freezing point compared to that of the pure solvent. The solid phase is in dynamic equilibrium with the liquid phase is the freezing point of the substance. It is defined as the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the substance in its liquid phase is equal to its vapour pressure in the solid phase.
Complete answer:
The properties of solutions depend on the decrease of vapour pressure are:
(1) relative lowering of the vapour pressure of the solvent
(2) depression of freezing point of the solvent
(3) elevation of a boiling point of the solvent
(4) osmotic pressure of the solution
Depression of freezing point: A solution will freeze when its vapour pressure equals the vapour pressure of the pure solid solvent. Thus, the freezing point of the solvent decreases.
Let Tfo&Tf be the freezing point of pure solvent and non-volatile solute respectively.
Then, depression in freezing point ΔTf=Tfo−Tf
The depression freezing point for a dilute solution is directly proportional to molality (m) of the solution. thus,
