Question
Question: Prove the given inverse trigonometric expression \({{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{63}{65} \right)={{\si...
Prove the given inverse trigonometric expression sin−1(6563)=sin−1(135)+cos−1(53).
Solution
We start solving this problem by first bringing sin−1(135) to the LHS and convert the given sine inverse functions, in the L.H.S, into cosine inverse functions. In the given two sine inverse functions, we assume the numerator as perpendicular and denominator as hypotenuse. Then we find the base in both the terms using Pythagoras theorem given by hypotenuse2=base2+perpendicular2. Then after converting them into cosine inverse, we use the formula cos−1x−cos−1y=cos−1(xy+1−x21−y2), if x,y≥0 and x2+y2≤1, and check if the values we got satisfy the assumed formula and find the value of it, thereby proving the given statement.
Complete step-by-step solution:
First let us change sin−1(6563) into cosine inverse function.
Let us assume that sin−1(6563)=α. Now let us find the value of cosα.
We know that, sinθ=HypotenusePerpendicular, therefore, θ=sin−1(HypotenusePerpendicular). On comparing we get that, in sin−1(6563), 63 is the perpendicular and 65 is the hypotenuse.
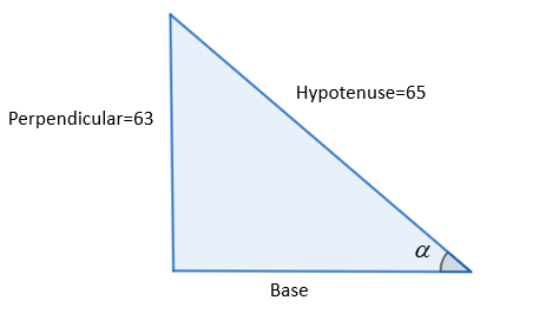
Using Pythagoras theorem given by: hypotenuse2=base2+perpendicular2, we have,
base2=hypotenuse2−perpendicular2⇒base=hypotenuse2−perpendicular2⇒base=652−632⇒base=(65+63)(65−63)⇒base=2×128⇒base=256⇒base=16
Now, we know that, cosθ=HypotenuseBase.
So, we get the value cosα=6516. Then we get,
⇒sin−1(6563)=α=cos−1(6516).............(1)
Similarly, let us change sin−1(135) into cosine inverse function.
Let us assume that sin−1(135)=β. Now let us find the value of cosβ.
In sin−1(135), 5 is the perpendicular and 13 is the hypotenuse.
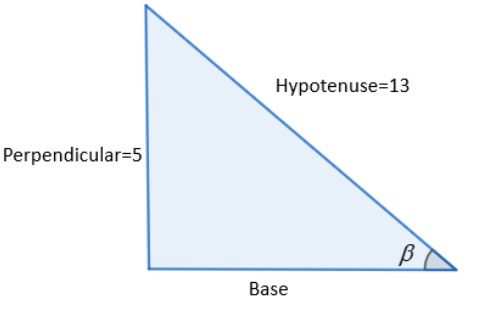
Using Pythagoras theorem given by: hypotenuse2=base2+perpendicular2, we have,
base2=hypotenuse2−perpendicular2⇒base=hypotenuse2−perpendicular2⇒base=132−52⇒base=169−25⇒base=144=12
So, we get the value cosβ=1312. Then we get,
⇒sin−1(135)=β=cos−1(1312).........(2)
From equations (1) and (2) we can say that,
⇒sin−1(6563)−sin−1(135)=cos−1(6516)−cos−1(1312)..........(3)
Now let us consider the value cos−1(6516)−cos−1(1312).
Now let us consider the formula, cos−1x−cos−1y=cos−1(xy+1−x21−y2) if x,y≥0 and x2+y2≤1.
Now let us verify if we can apply this formula or not.
Here x=6516 and y=1312 are greater than zero.
⇒(6516)2+(1312)2⇒4225256+169144⇒4225256+3600⇒42253856≤1
So, we can use the above formula. Then we get,
