Question
Question: Prove that \(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} \dfrac{{\sin x}}{x} = 1\) ( \(x\) being measured in ra...
Prove that x→0limxsinx=1 ( x being measured in radians).
Solution
Sandwich theorem is useful in proving the limits given in the question.
Theorem: Sandwich Theorem:
Let f,g and h be real functions such that g(x)⩽f(x)⩽h(x) for all x in the common domain of definition.
For some limit a, if x→alimg(x)=l=x→alimh(x), then x→alimf(x)=l. This can be illustrated as the following:
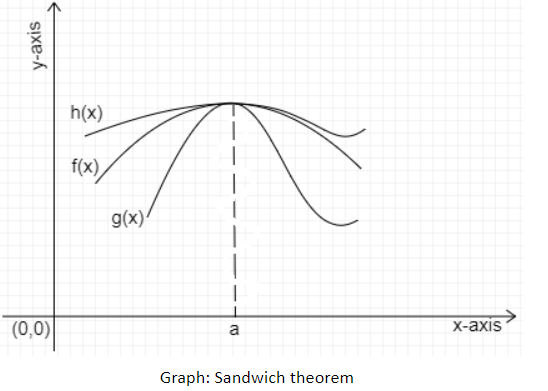
Try to prove the inequality relating to trigonometric functions. cosx<xsinx<1, and the given limit can be easily proved by the sandwich theorem.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Prove the inequality cosx<xsinx<1
Consider figure 1.
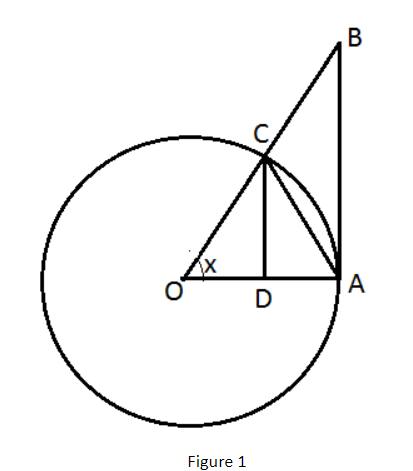
In figure 1, O is the center of the unit circle such that the angle ∠AOC is x radians and 0<x<2π.
Line segment BA and CD are perpendicular to OA.
Further, join AC. Then
Area of △AOC < area of sector OAC < area of △AOB
The area of a triangle is half of the product of base and height.
Area of a sector of a circle = 2πθ(πr2), where θ is the angle of the sector.
⇒21OA.CD<2πxπ(OA)2<21OA.AB
⇒CD<x(OA)<AB …… (1)
In △OCD
sinx=hypotenuseperpendicular
Therefore, sinx=OCCD
The line segments OC and OA are the radius of the circle with center O in figure 1.
Thus, OC = OA
Therefore, sinx=OACD
Hence, CD=OAsinx
In △AOB
tanx=baseperpendicular
Therefore, tanx=OAAB
Hence, AB=OAtanx
Put the values of CD and AB in the inequality (1)
⇒OAsinx<x(OA)<OAtanx
We know tanx=cosxsinx
⇒sinx<x<cosxsinx
Dividing throughout by sinx, we get:
⇒1<sinxx<cosx1
Take reciprocals throughout, we have:
⇒cosx<xsinx<1
Step 2: Use sandwich theorem to prove the given limit
We know that x→alimcos(f(x))=cosx→alim(f(x))
Thus, the x→0limcosx=cosx→0lim(x)
Therefore, cos0=1
Hence, x→0limcosx=1
And x→1lim1=1
We have, x→0limcosx=1=x→0lim1
Then x→0limxsinx=1 by the sandwich theorem.
The limit x→0limxsinx=1 has been proved.
Note:
Use the above limit x→0limxsinx=1 for future questions. For example:
Evaluate: x→0limsin2xsin4x
Multiplying and dividing by 4x and make the angles in the sine function and dividing angle the same.
⇒x→0lim[4xsin4x×sin2x2x×2]
