Question
Question: Prove that: \(2{\sin ^2}\dfrac{\pi }{6} + {\operatorname{cosec} ^2}\dfrac{{7\pi }}{6}{\cos ^2}\dfr...
Prove that:
2sin26π+cosec267πcos23π=23
Solution
Note that, since 67π is in third quadrant, therefore cosec67π is negative.
Then in the left hand side, substitute the values of sin6π, cosec67π and cos3π.
And on solving we get the desired result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given to prove that 2sin26π+cosec267πcos23π=23
Left hand side is given by,
2sin26π+cosec267πcos23π
The above expression can be written as,
=2sin26π+cosec2(π+6π)cos23π
Since, 67π is in the third quadrant, therefore cosec67π is negative,
=2sin26π+(−cosec6π)2cos23π
On simplification we get,
=2sin26π+cosec26πcos23π
Using sin6π=21,cos3π=21,cosec6π=2, we get,
=2×(21)2+(2)2×(21)2
On squaring we get,
=(2×41)+(4×41)
On simplification we get,
=21+1
=23
= Right hand side
Hence, 2sin26π+cosec267πcos23π=23 (proved).
Note: Note the following important formulae:
1.cosx=secx1 , sinx=cosecx1 , tanx=cotx1
2.sin2x+cos2x=1
3.sec2x−tan2x=1
4.cosec2x−cot2x=1
5.sin(−x)=−sinx
6.cos(−x)=cosx
7.tan(−x)=−tanx
8.sin(2nπ±x)=sinx , period 2π or 360∘
9.cos(2nπ±x)=cosx , period 2π or 360∘
10.tan(nπ±x)=tanx , period π or 180∘
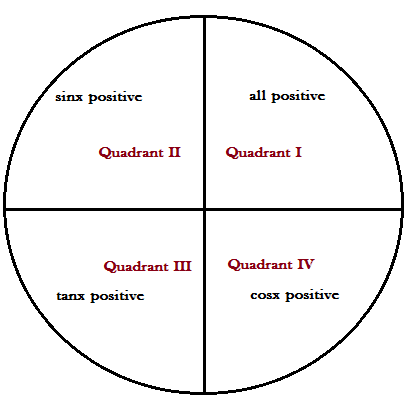
Sign convention:
sin2x=2sinxcosx
cos2x=cos2x−sin2x=1−2sin2x=2cos2x−1
tan2x=1−tan2x2tanx=cotx−tanx2
Also, the trigonometric ratios of the standard angles are given by
| 0∘| 30∘| 45∘| 60∘| 90∘
---|---|---|---|---|---
Sinx| 0| 21 | 21 | 23 | 1
Cosx| 1| 23| 21| 21| 0
Tanx| 0| 31 | 1| 3| Undefined
Cotx| undefined| 3| 1| 31| 0
cosecx| undefined| 2| 2| 32| 1
Secx| 1| 32| 2| 2| Undefined
