Question
Question: Prove \(\cos \left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} + x} \right)\cos \left( {2\pi + x} \right)\left[ {\cot \left...
Prove cos(23π+x)cos(2π+x)[cot(23π−x)cot(2π+x)]=1.
Solution
Hint : Here, in the given question, we need to prove that cos(23π+x)cos(2π+x)[cot(23π−x)cot(2π+x)]=1. Here we are given a trigonometric function, we need to know how a function can be represented in terms of other functions so that we can simplify and prove the given function. For the given question, first we will solve the given functions individually and try to convert them into the simplest form using identities. After this, we will try to represent the cot function in terms of cos and after that we will simplify the given function to prove that LHS is equal to RHS.
Complete step-by-step answer :
To prove: cos(23π+x)cos(2π+x)[cot(23π−x)cot(2π+x)]=1.
L.H.S. = cos(23π+x)cos(2π+x)[cot(23π−x)cot(2π+x)]
First we will solve, cos(23π+x)
Putting π=180∘, we get
=cos(23×180∘+x)
On simplification, we get
=cos(270∘+x)
It can also be written as,
=cos(360∘−90∘+x)
As we know 360∘=2π, we get
=cos(2π+(x−90∘))
As we know cos(2π+x)=cosx. Therefore, we get
=cos(x−90∘)
On taking negative sign as common, we get
=cos(−(90∘−x))
As we know cos(−x)=cosx. Therefore, we get
=cos(90∘−x)
As we know cos(90∘−θ)=sinθ (Here, sin is positive because 90∘−θ lies in the first quadrant, and in first quadrantsin is positive). Therefore, we get
Therefore, we get
=sinx
Now, cos(2π+x)=cosx
Now we solve, cot(23π−x)
Putting π=180∘
=cot(23×180∘−x)
On simplification, we get
=cot(270∘−x)
It can also be written as,
=cot(360∘−90∘−x)
As we know 360∘=2π, we get
=cot(2π−90∘−x)
On taking negative sign as common, w get
=cot(2π−(x+90∘))
As we know cot(2π−x)=−cotx. Therefore, we get
=−cot(x+90∘)
As we know cot(90∘+θ)=−tanθ (Here, tan is negative because 90∘+θ lies in the second quadrant, and in second quadrant tan is negative). Therefore, we get
=−(−tanx)
=tanx
Now, cot(2π+x)=cotx
Putting these values in the equation
cos(23π+x)cos(2π+x)[cot(23π−x)cot(2π+x)]
=(sinx)×(cosx)×[tanx+cotx]
Now, we will represent tan and cot in terms of sin and cos. As we know tanx=cosxsinx and cotx=sinxcosx. Therefore, we get
=(sinxcosx)×[cosxsinx+sinxcosx]
On taking LCM, we get
==(sinxcosx)×[cosxsinxsinx×sinx+cosx×cosx]
=(sinxcosx)×[sinxcosxsin2x+cos2x]
As we know that sin2x+cos2x=1, thus we get
=(sinxcosx)×[sinxcosx1]
On multiplication, we get
=sinxcosxsinxcosx
On cancelling out common terms, we get
=1
= R.H.S.
Hence proved.
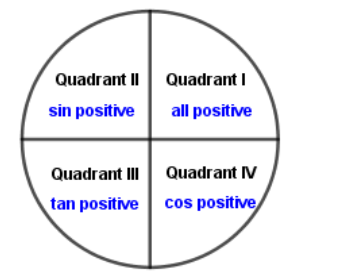
Note : To solve the questions related to trigonometric functions, one must remember all the standard formulas of trigonometric functions. Most of the trigonometric functions questions are just based on substitutions, we can only solve the problem if we know the formulas and sign convention. We should know signs of trigonometric ratios in different quadrants. The easiest way to memorise the signs of trigonometric ratios in different quadrants is the four-word phrase ‘ALL SCHOOL TO COLLEGE’. The first letter of the first word in the phrase is A, indicating that all trigonometric ratios are positive in the first quadrant. The first letter of the second word in the phrase is S, indicates that sine and its reciprocal is positive in the second quadrant. The first letter of the third word in the phrase is T, indicates that tangent and its reciprocal is positive in the third quadrant. The first letter of the fourth word in the phrase is C, indicates that cosine and its reciprocal is positive in the fourth quadrant.