Question
Question: Propyne and propene can be distinguished by: A. Conc.\({{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{4}}\) ...
Propyne and propene can be distinguished by:
A. Conc.H2SO4
B. Br2 in CCl4
C. Dilute KMnO4
D. AgNO3 in ammonia
Solution
The chemical reagents give differences in chemical compounds. Concentrated sulphuric acid and bromination show additional reactions. Dilute potassium permanganate gives carboxylic acids on reaction with one and alcohols with another. Ammoniacal silver nitrate removes acidic hydrogen to give precipitates.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us discuss the products formed when propyne and propene react with the reagents given in the options:
(A) Conc.H2SO4: Propyne reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid in presence of mercuric sulphate to form acetone in equilibrium with its tautomeric structure. The reaction is
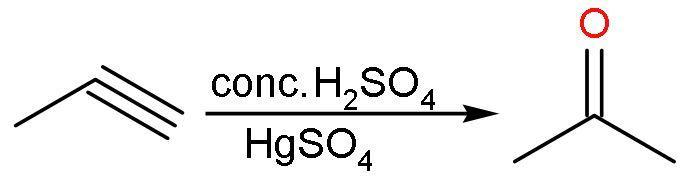
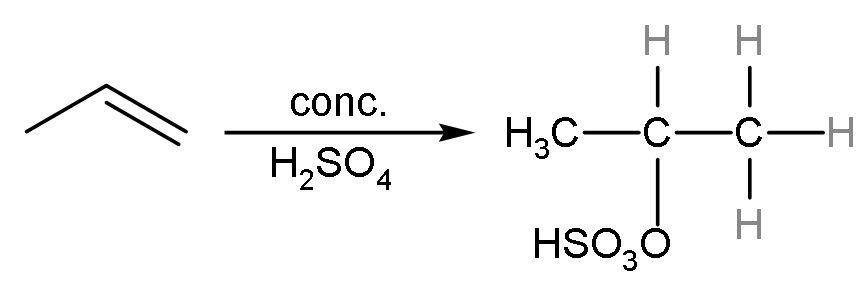
Propene reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid to give an additional reaction. In this reaction, H+ of sulphuric acid adds to more hydrogenated double-bonded carbon and −OSO3H to less hydrogenated carbon atom. The reaction is
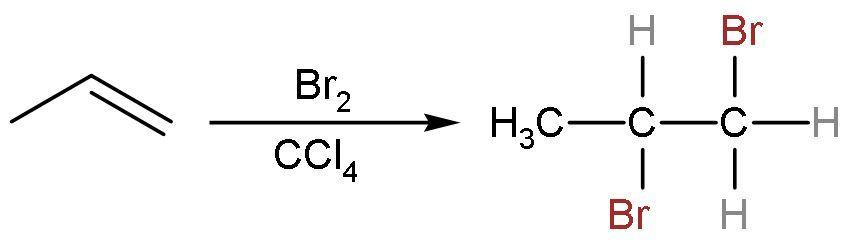
(B) Br2 in CCl4: Propene is an unsaturated compound. So, it gives an additional reaction with bromine in a nonpolar solvent of carbon tetrachloride. The double bond is replaced by the single bond between the carbon atoms and additions of bromine atoms on both the double-bonded carbon atoms take place. The reaction is
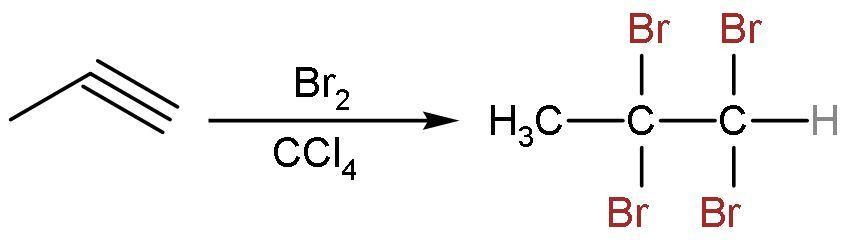
Similarly, propyne reacts with Br2 in CCl4 to give addition reaction only. Here, the triple bond is replaced by the single bond. The 2 moles of Br2 in CCl4 will be needed here. The reaction is
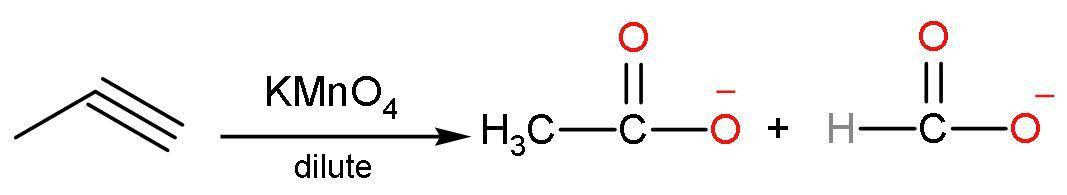
(C) Dilute KMnO4: In this reaction, propyne reacts with potassium permanganate to give carboxylic acids of lesser carbon atoms. It means that the triple bond is broken from the presence of a triple bond. The reaction is
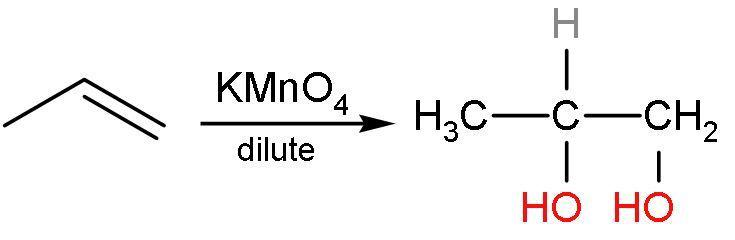
Propene reacts with potassium permanganate to give an additional reaction. In this, the hydroxyl groups are added to both the double-bonded carbon atom. This is vicinal diols or 1,2-diols. The double bond is replaced by the alcohol groups. The reaction is
(D) AgNO3 in ammonia: Propene does not react with ammoniacal silver nitrate.
Propyne, on the other hand, gives this reaction. Propyne has a triple bond between C1−C2. This means that the alkyne is terminal. Terminal alkynes have acidic hydrogens. These hydrogens are removed and insoluble precipitates are formed. The reaction is
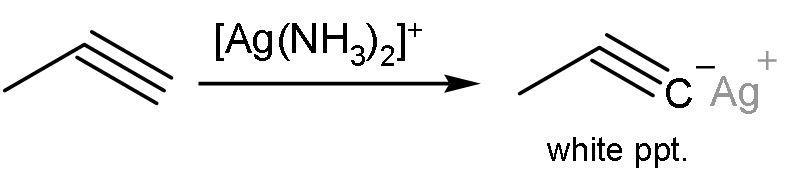
Propyne and propene can be distinguished by AgNO3 in ammonia, which is option ’d’.
So, the connected answer is (D).
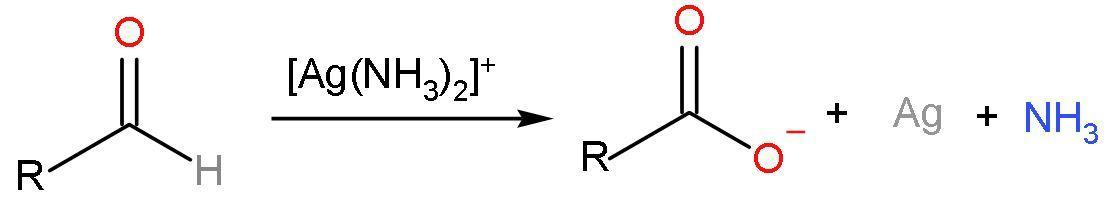
Note: Aldehydes are oxidised by diamine silver ions [Ag(NH3)2+] or ammoniacal silver nitrate solution to carboxylic acids. This reagent is also known as Tollen’s reagent. The reaction forms out of a silver mirror as a product to confirm the presence of aldehydes. The reaction is