Question
Question: Propyne and propene can be distinguished by: A. Conc. \({H_2}S{O_4}\) B. \(B{r_2}\) in \(CC{l_4}...
Propyne and propene can be distinguished by:
A. Conc. H2SO4
B. Br2 in CCl4.
C. Dil. KMnO4
D. AgNO3 in ammonia.
Solution
Hint: Silver nitrate in ammonia is actually Tollen’s reagent. It also reacts with acidic hydrogens to give precipitates.
Complete step by step answer:
To get the answer, let us check each reaction one by one:
Conc. H2SO4:
Propyne on reaction with conc. H2SO4 produces a ketone.
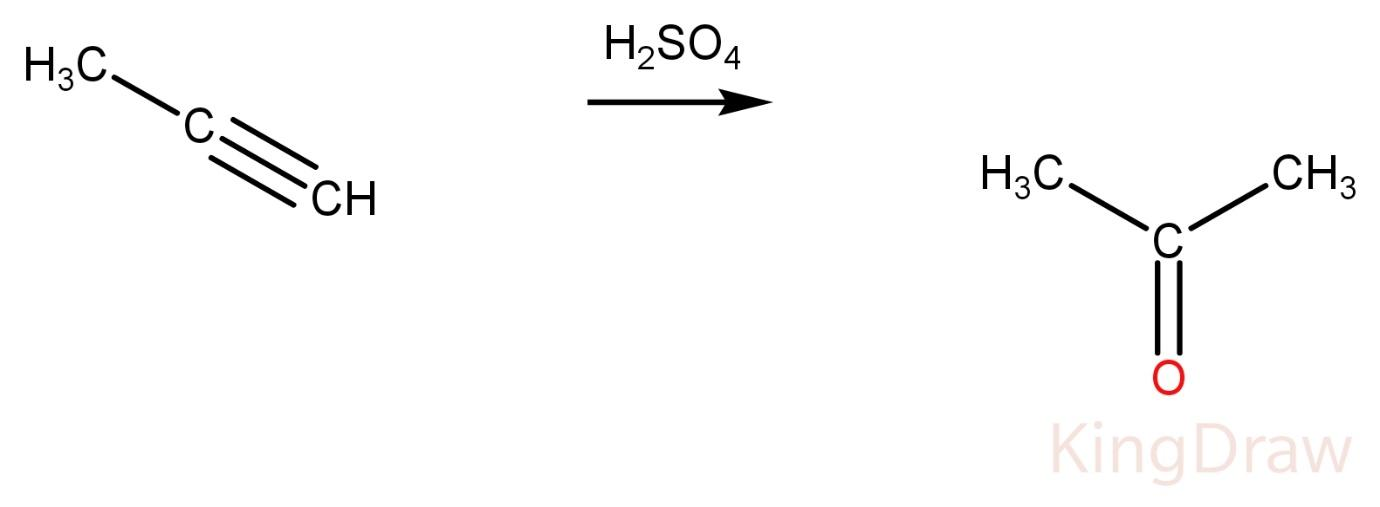 Propene on reaction with conc. H2SO4 produces alcohol.
Propene on reaction with conc. H2SO4 produces alcohol.
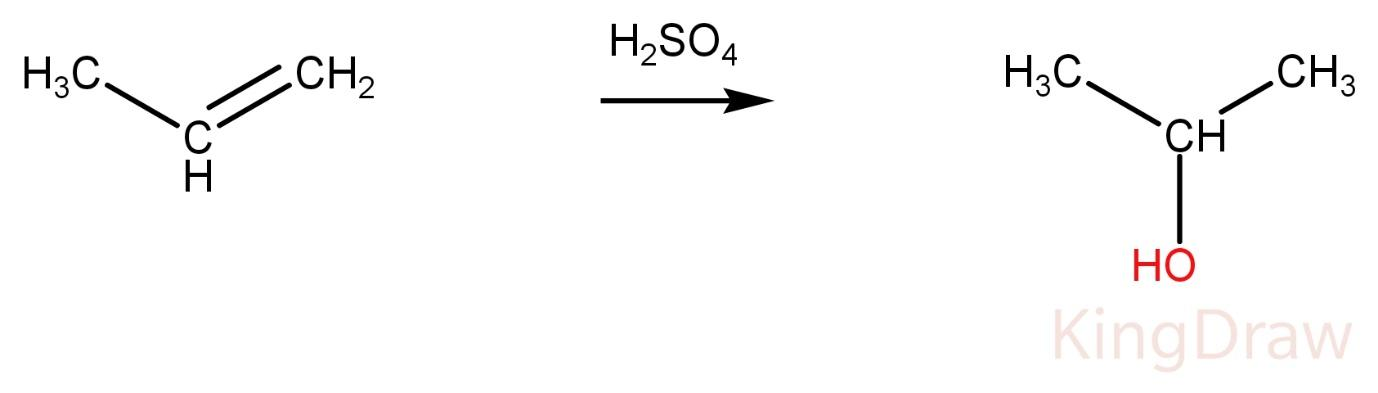 Ketone and alcohol can’t be distinguished at this condition without adding any other reagent. Hence, it is not the correct option.
Ketone and alcohol can’t be distinguished at this condition without adding any other reagent. Hence, it is not the correct option.
Br2]in[CCl4:
Propyne on reaction with Br2 in CCl4 produces a vicinal dibromo alkene whereas propene on reaction with Br2 in CCl4 produces a vicinal dibromo alkane.
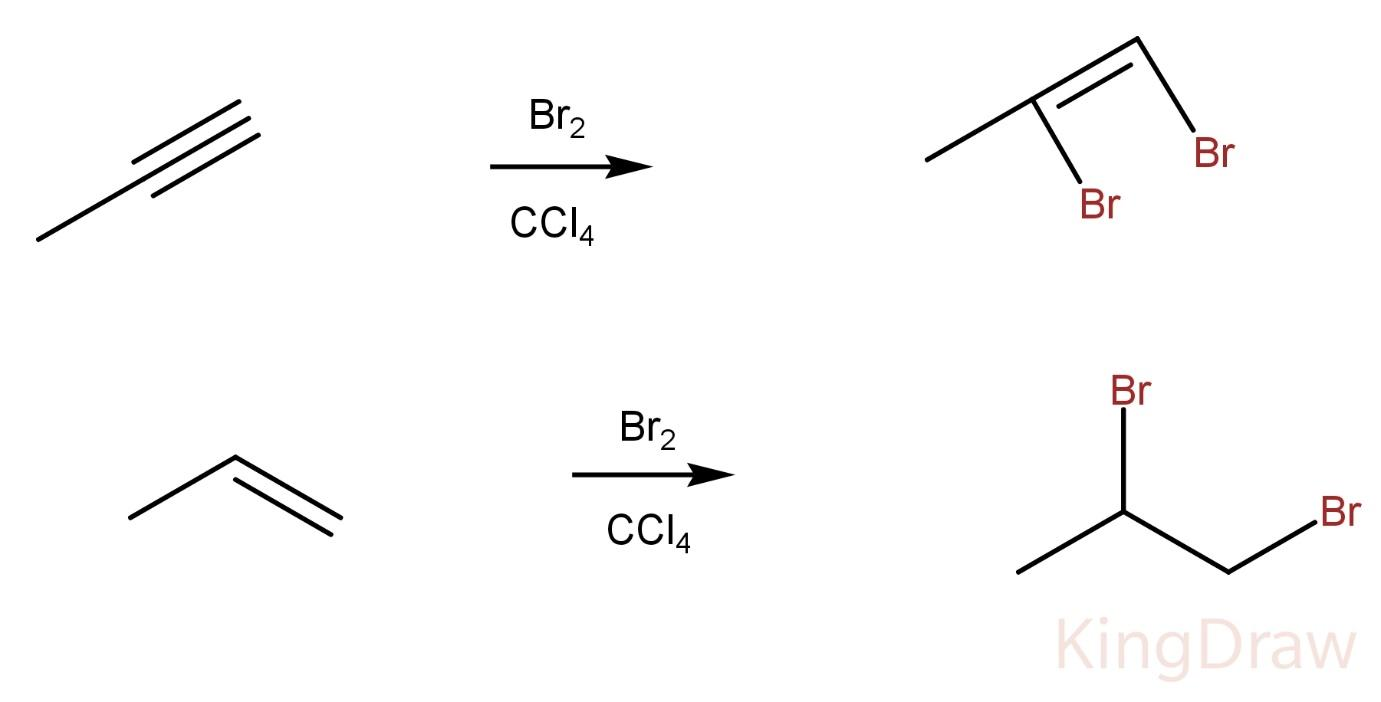 Hence, the two compounds can’t be distinguished by this process.
Hence, the two compounds can’t be distinguished by this process.
Dil. KMnO4:
Propynes on reaction with Dil. KMnO4 produce -ketoacid.
Propene on reaction with Dil. KMnO4 produce a vicinal diol. 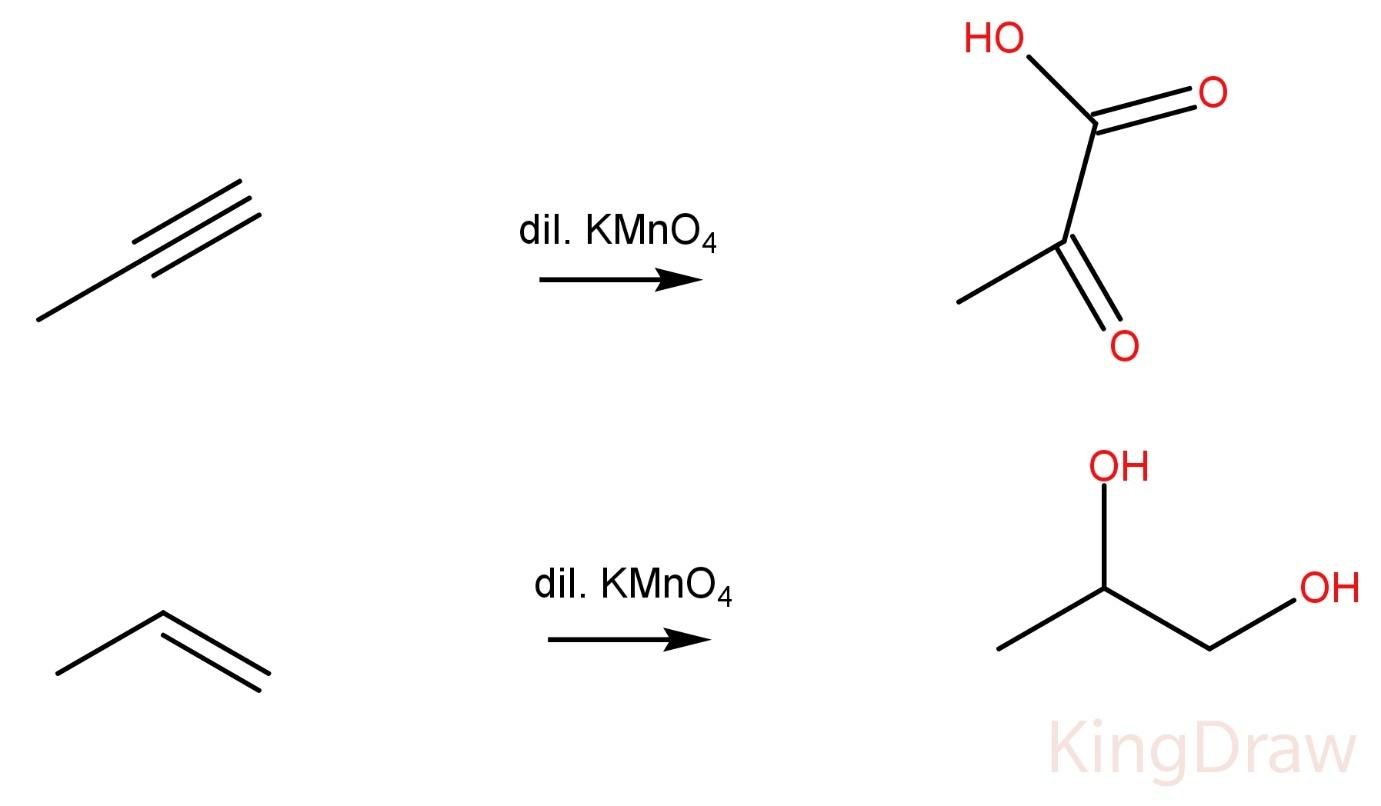 Hence, the two compounds cannot be distinguished by this method also.
Hence, the two compounds cannot be distinguished by this method also.
AgNO3 in ammonia:
Propyne on reaction with AgNO3 in ammonia produces a white precipitate, while propene does not show any reaction with the Tollen’s reagent.
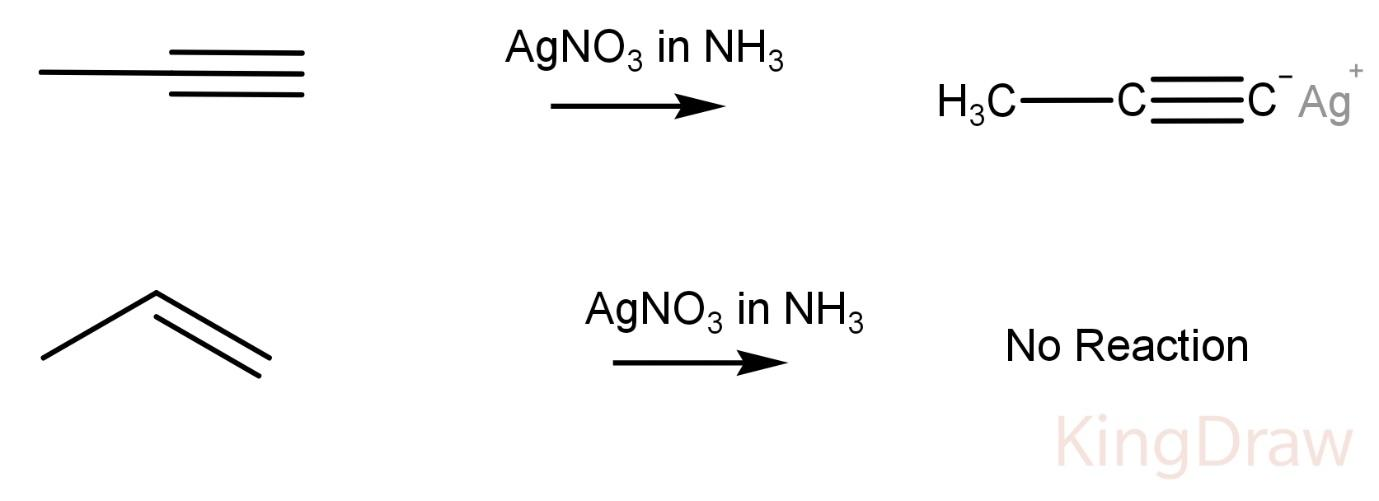
This is due to the fact that Tollen’s reagent reacts with an acidic hydrogen forming a precipitate like in a propyne. The hydrogen which is replaced is very acidic due to high electronegativity of an sp hybridized carbon.
Hence, this reagent can be used to distinguish between a propyne and a propene.
Therefore, the correct answer is (D) AgNO3 in ammonia.
Note: When an alkyne is reacted with conc. Sulphuric acid, ketone is formed by the Markovnikov addition of -OH, followed by the rearrangement of the alcohol formed from enol form to keto.
