Question
Question: Propyl acetate, \({C_5}{H_{10}}{O_2}\) gives the odour and taste to pears. How many moles of \(C\) a...
Propyl acetate, C5H10O2 gives the odour and taste to pears. How many moles of C are present in 1.50 moles of propyl acetate?
Solution
For one mole of a compound, the number of moles of an element in that compound is equivalent to the number of atoms of that element present. For example, in the mole of methane i.e., CH4the number of moles of carbon atom and hydrogen atom will be equivalent to 1 and 4 moles respectively.
Complete answer:
Propyl acetate is an example of ester and due to its sweet smell and taste, it gives the odour and taste to pears and is also used in fragrances and as additive flavours. The molecular formula of propyl acetate is C5H10O2 and structurally it is represented as follows:
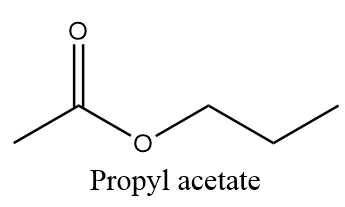
Now, as per question, we need to find out the number of moles of carbon present in 1.50 moles of propyl acetate. So, the calculation is done in the following way:
Number of moles of carbon in 1 mole of C5H10O2⇒5moles
Therefore, the number of moles of carbon in 1.50 moles of C5H10O2⇒5×1.50=7.5 moles.
Hence, 7.5 moles of C are present in 1.50 moles of propyl acetate.
Note:
Ensure not to get confused between the mass percentage of an element and the number of moles of an element in a compound. The mass percentage of an element in a compound is equal to the ratio of actual amount of that element (i.e., the number of atoms of the element present multiplied by its molar mass) to the molar mass of the compound multiplied by 100 whereas the number of moles of an atom is equivalent to stoichiometric ratio in which it is present.
