Question
Question: \[Propanoic\;acid \xrightarrow[H_2O]{Cl_2/Red\;P} {\rm{X}}\]. What is \[{\rm{X}}\]? A) Propanal ...
PropanoicacidCl2/RedPH2OX.
What is X?
A) Propanal
B) Propanol
C) propane
D) α− chloro propanoic acid
Solution
We know that the reaction of carboxylic acid which must have α− hydrogen atom with bromine or chlorine results in the formation of 2− bromo carboxylic acid or 2− chloro carboxylic acid in the presence of red phosphorus. The halogenation takes place during the reaction at the α− carbon atom.
Complete answer:
This reaction is carried out on the basis of Hell - Volhard - Zelinsky halogenation reaction halogenated carboxylic acids at the α carbon atom.
We know that propanoic acid is the carboxylic acid with α− hydrogen atom. The reaction of propanoic acid with chlorine in the presence of red phosphorus leads to the formation of 2−chloropropanoic acid which is also named as α−chloro propanoic acid because the chlorination will take place at α−carbon atom.
We can write the chemical equation for the reaction carried as follows.
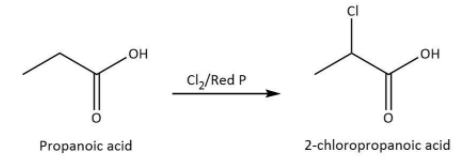
Hence, we can conclude that the correct option is D.
Note: The reaction which is carried out in the above question is commonly known as Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction. The reaction takes place by the formation of phosphorous trichloride as the in-situ which catalysis the reaction. Therefore, we can say that the reaction is acid catalyzed enolization which is followed by the chlorination at alpha position.
