Question
Question: Product obtained in following reactions \((1),(2)\And (3)\) is: ,(2)&(3) is:
(a) A=B,C is different
(b) A=C,B is different
(c) B=C,A is different
(d) A=B=C is same
Solution
Alcoholic potassium hydroxide KOH acts as a strong base; it is used in the elimination reactions where unsaturated products are obtained from saturated compounds.
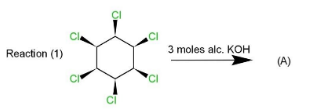
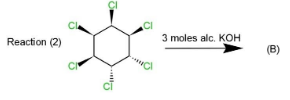
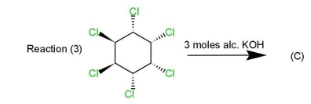
Complete step by step solution: Three reactions (1),(2)&(3) are given that involves 1,2,3,4,5,6− chloro cyclohexane, which is treated with three moles of alcoholic potassium hydroxide. The reaction is a type of β− elimination reaction that results in double bonds in the product.
The first reaction is accompanied by the removal of hydrogen fromβ− position which is at the anti position, so this will be the type of E2 anti-elimination reaction. This reaction is carried in the way that alternate double bond formation takes place when β− hydrogens from 1,3,5 positions get removed along with chlorine from 2,4,6 positions as 3 moles of KOH are used. Hence the product formed will be 1,3,5 trichlorobenzene.
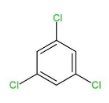
This product will be obtained in the first case. While in the second and third case, the product obtained will be the same as in reaction (2) four Cl atoms are on the same side while two are on opposite sides which will retain the symmetry and 1,3,5 trichlorobenzene. Same will happen in reaction (3) as four Cl atoms are on the same side and two on the opposite. The geometry in all the three reactions will be such that the elimination will occur of Cl and hydrogen to retain Cl at 1,3,5 positions along with double bonds.
Therefore, option (d) is correct as products A=B=C are the same.
Note: Anti-elimination takes place when the β− hydrogen is removed from the opposite side to that of the leaving group (here chlorine). Syn elimination takes place when β− hydrogen is removed from the same side to that of the leaving group.
