Question
Question: Product formed is? 
(a)
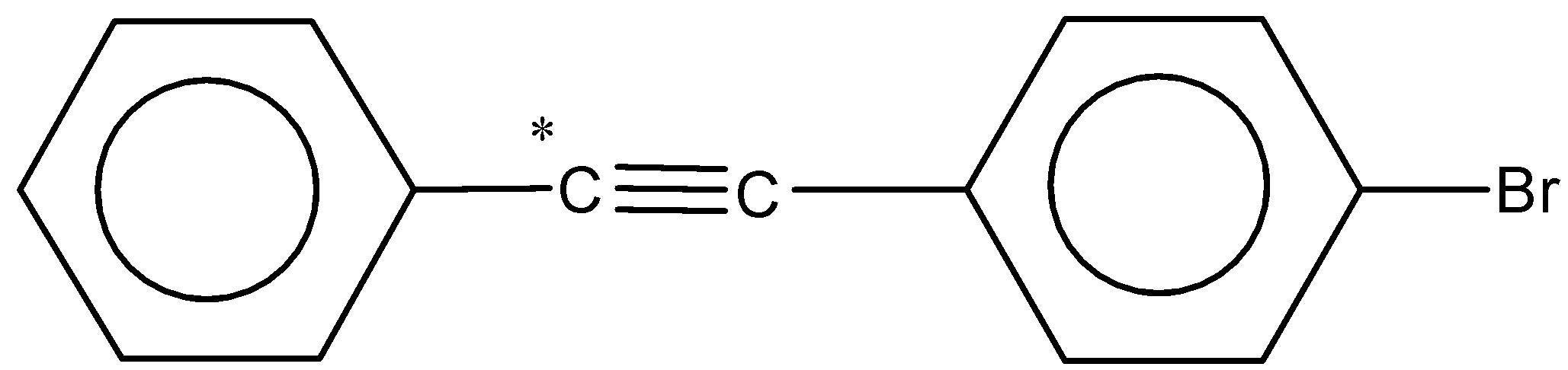
(b)
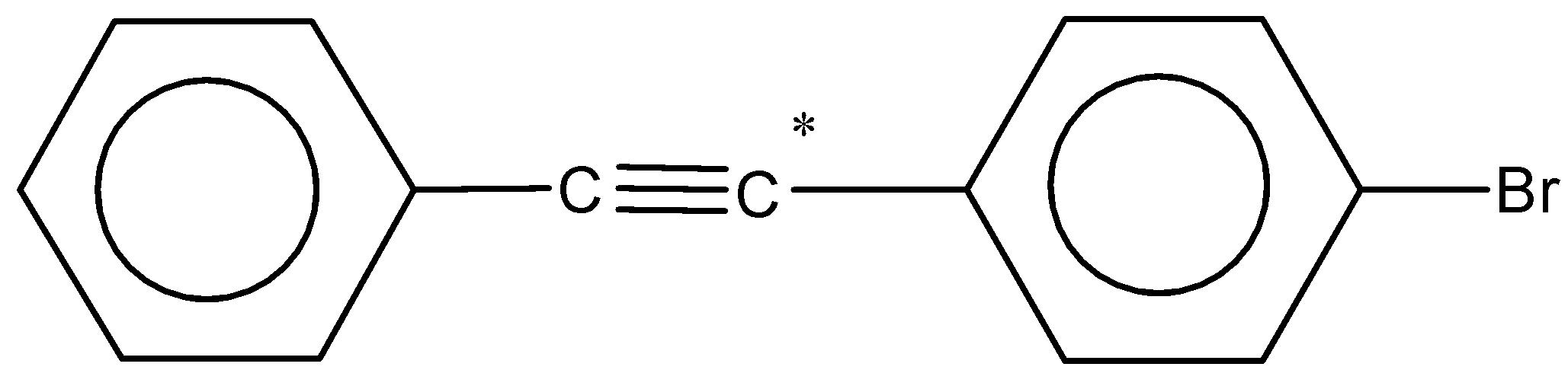
(c)
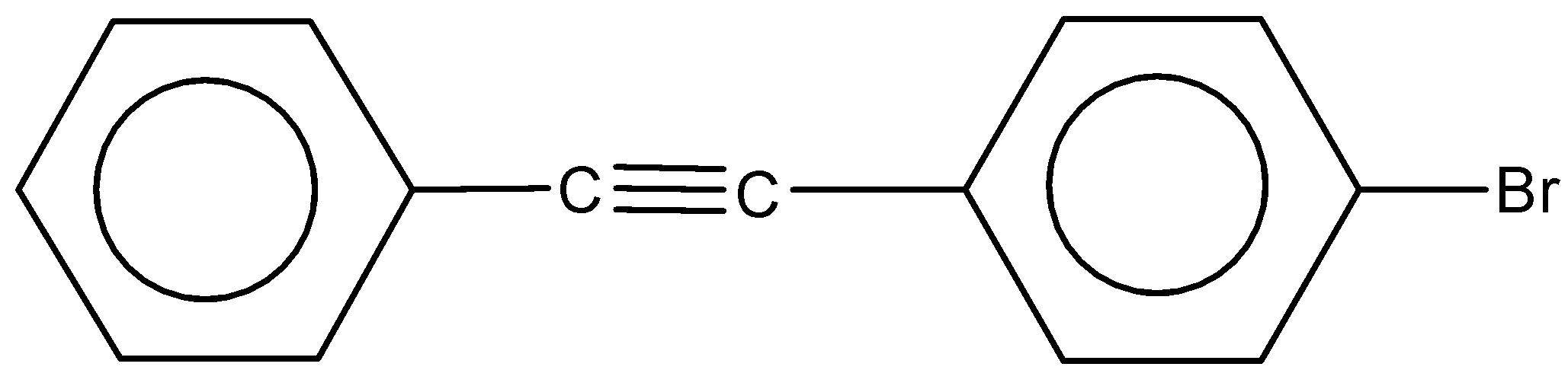
(d)
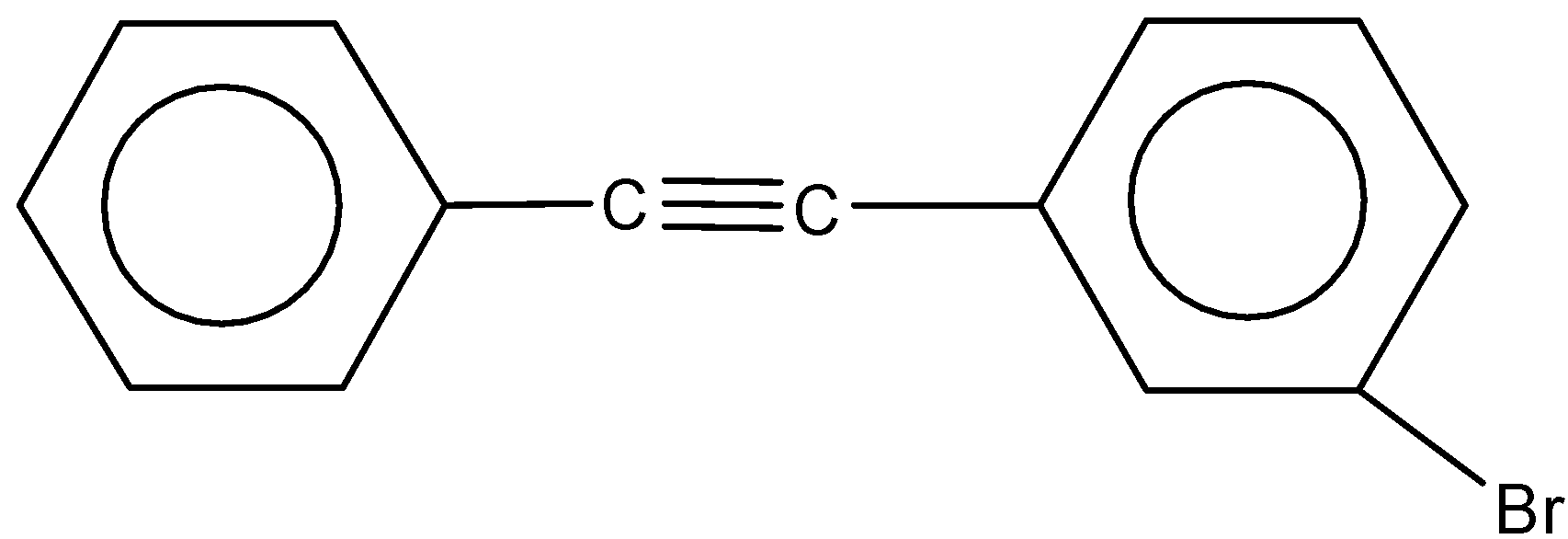
Solution
The answer here is based on the basic concept of organic chemistry that deals with the named reactions and also the reagent used for this tertiary butoxide where this is a strong base that catalyses the reaction of hydrosilanes and heterocyclic compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
- We have come across the chapters of organic chemistry that deal with the basic concepts that include the basic named reactions and also some reactions like oxidation, reduction and related reactions.
- Now, we shall see what the potassium tertiary butoxide is and how it acts as a strong base.
In the above question, the alkene attached to two phenyl rings and another carbon attached to bromine and on treating this with potassium tertiary butoxide, the reaction taking place gives the Hoffmann’s product that is elimination reaction takes place to form less substituted alkenes.
- The reaction taking place when tertiary butoxide that is a strong base where it abstracts the proton according to Hoffman’s rule that is from the less substituted carbon atom to give the migratory product is as shown below:

Accordingly, in this above reaction, the tertiary butoxide ion abstracts a hydrogen of less substituted alkene and the formation of triple bond takes place by the migration of the phenyl ring to the other carbon in order to balance the valency of carbon.So the correct answer is “B”:
Note: Note that migratory aptitude of the aromatic rings is based on the presence or absence of the electron donating or electron withdrawing group and in this above reaction, the electron withdrawing bromine does not favour the migration.
