Question
Question: Product formed in the reaction is: 
Solution
The given compound is a primary alcohol, it is reacting with PCl3. Phosphorus trichloride (PCl3) is a colourless liquid. In this reaction the (-OH) group of alcohol is replaced by the (-Cl) group of phosphorus trichloride.
- On reacting with the chlorine derivative of alcohol gives substitution reaction with the sodium methoxide.
- Lesser the steric hindrance faster will be the rate of bimolecular substitution reaction (SN2). (SN2) Prefers the less hindered side to attack. So ease of (SN2) reaction is (1∘2∘3∘).
(SN2) Reactions involve inversion of configuration of compound stereochemically. So 1∘ alkyl halide is preferred to (SN2) reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
This reaction is completed in two steps-
PCl3 (Phosphorus trichloride) is good chlorinating agent; it reacts quickly with alcohols and performs substitution reaction.
- In the first step chlorination of substrate takes place in which hydroxyl group of substrate compound is replaced by chlorine atom. This reaction is represented through following chemical reaction-
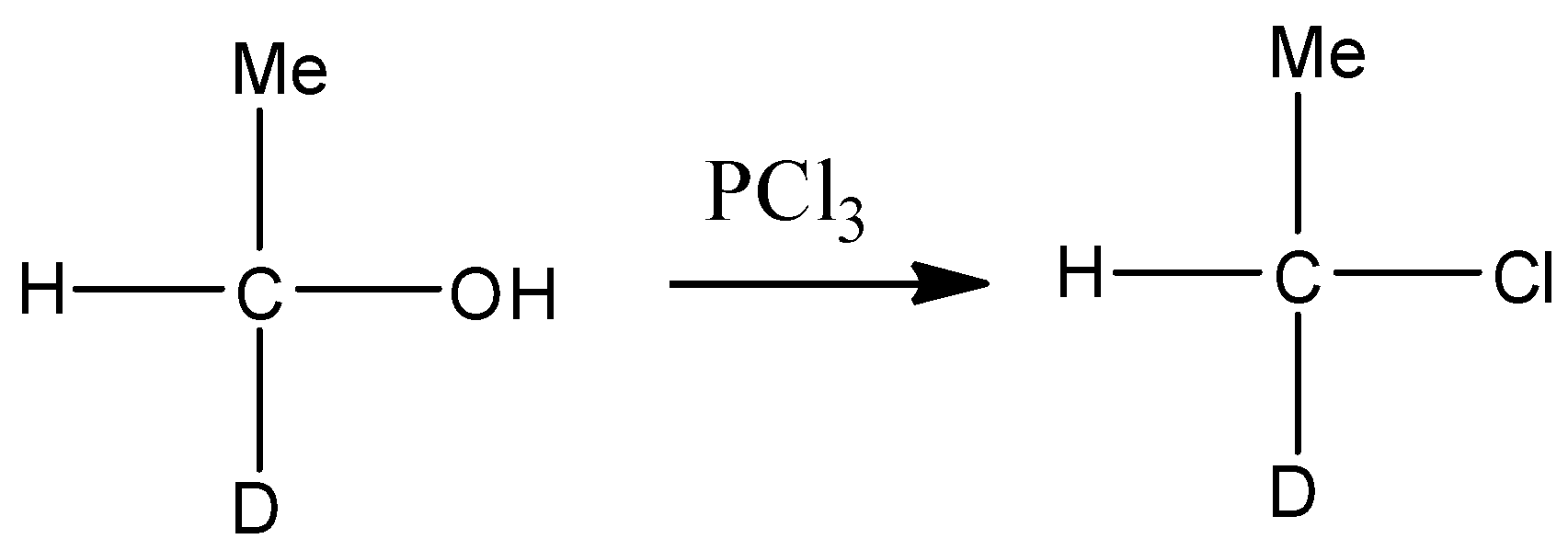
In the second step the chlorinated product of alcohol treated with sodium methoxide in the strong basic medium (NaOH) . Since chlorine is a poor leaving group, in the presence of polar solvent it gives bimolecular substitution reaction and forms ether. This reaction is represented through the following chemical equation.
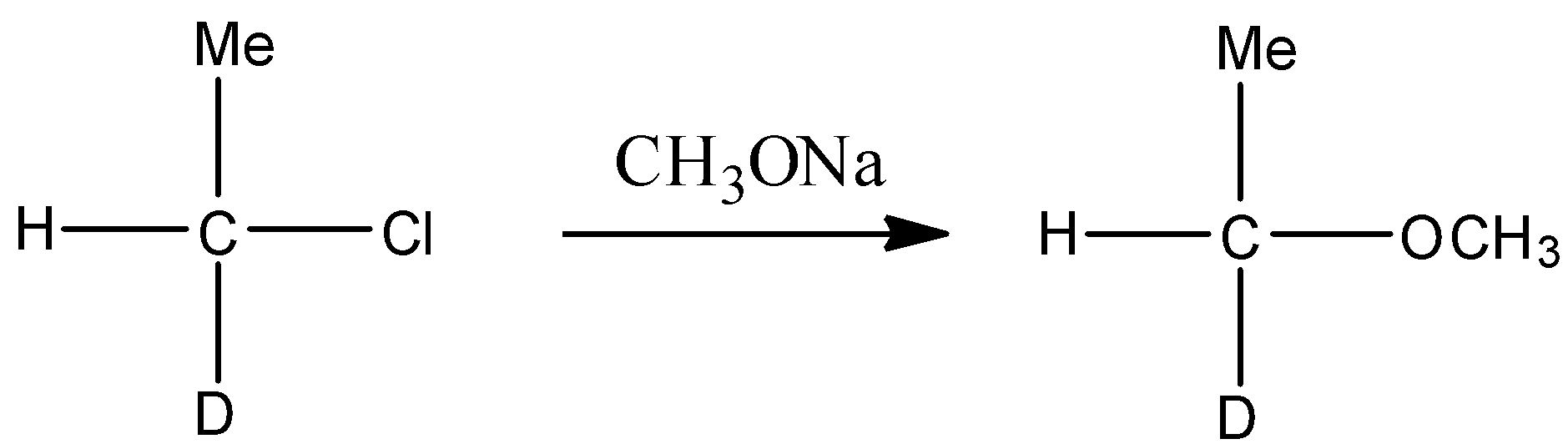
Note: - Sterically unhindered primary alkyl haloalkane mainly gives nucleophilic substitution reaction, while sterically hindered (branched primary, secondary and tertiary haloalkane mainly gives elimination reaction.
- Sterically unhindered nucleophiles mainly give substitution reactions. Branched or bulky substrate mainly gives a unimolecular substitution reaction (SN1).
