Question
Question: Product \(A\) in the below reaction is, \({C_6}{H_5}N{H_2} + CHC{l_3} + KOH \to A + KCl + {H_2}O\)...
Product A in the below reaction is,
C6H5NH2+CHCl3+KOH→A+KCl+H2O.
A) 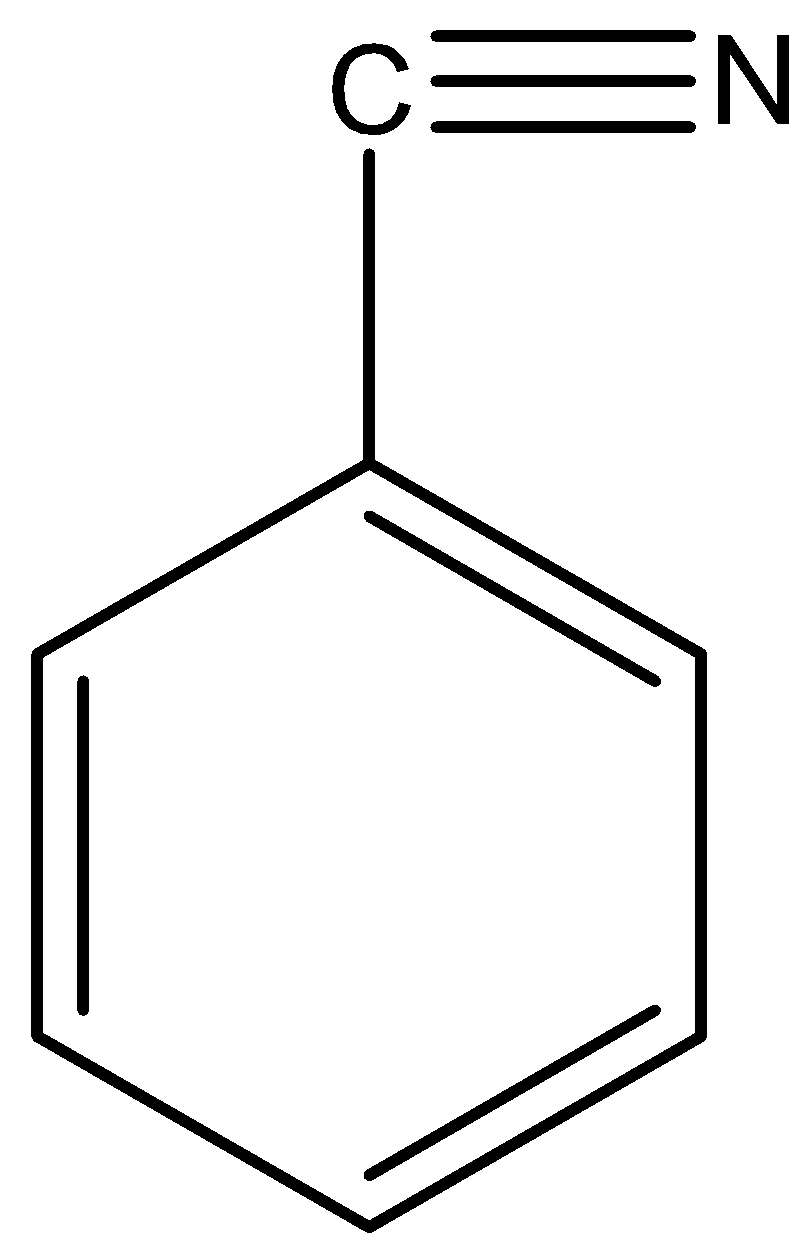
B) 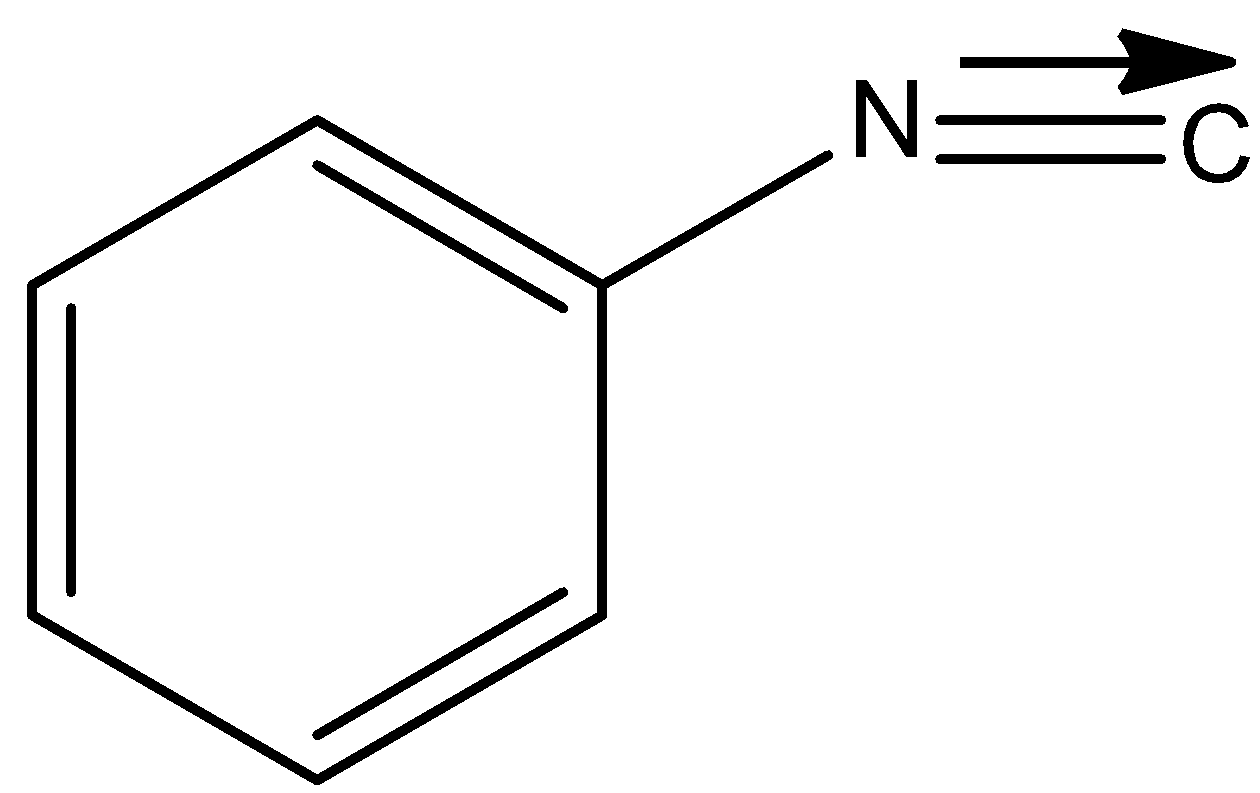
C) 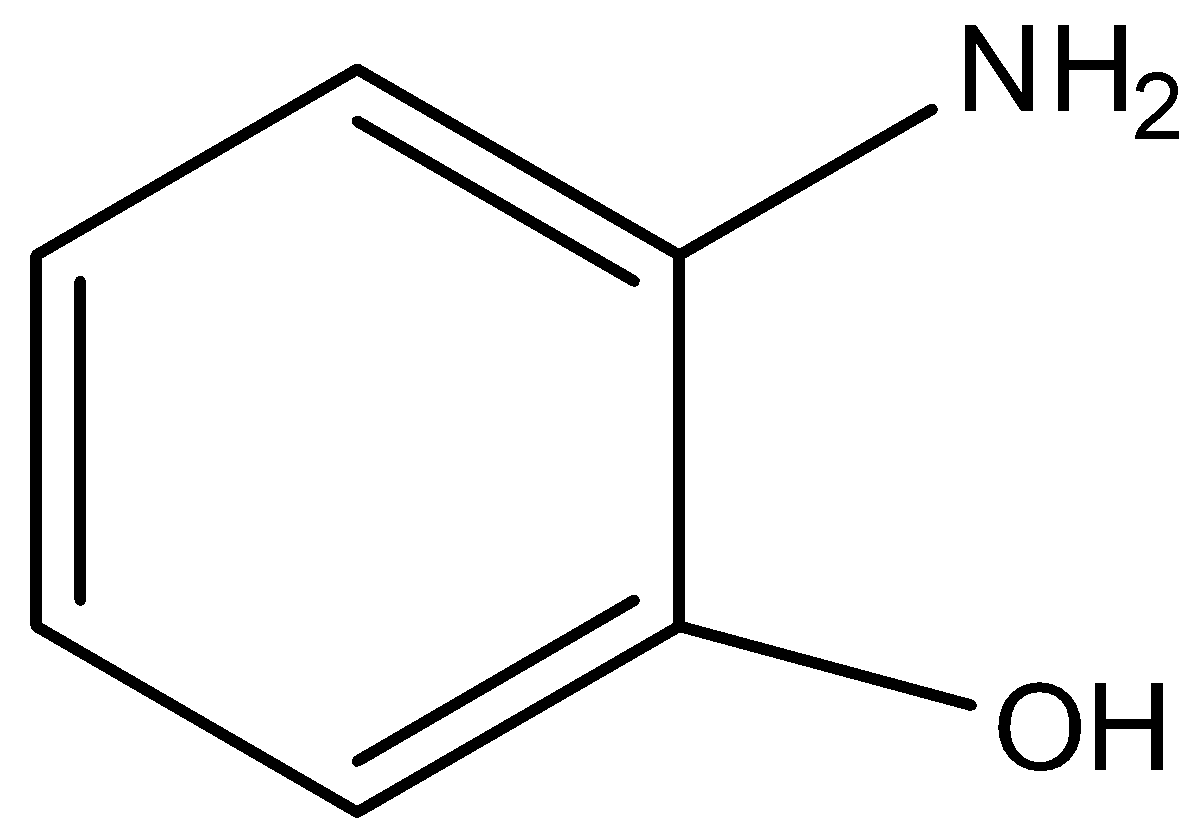
D) 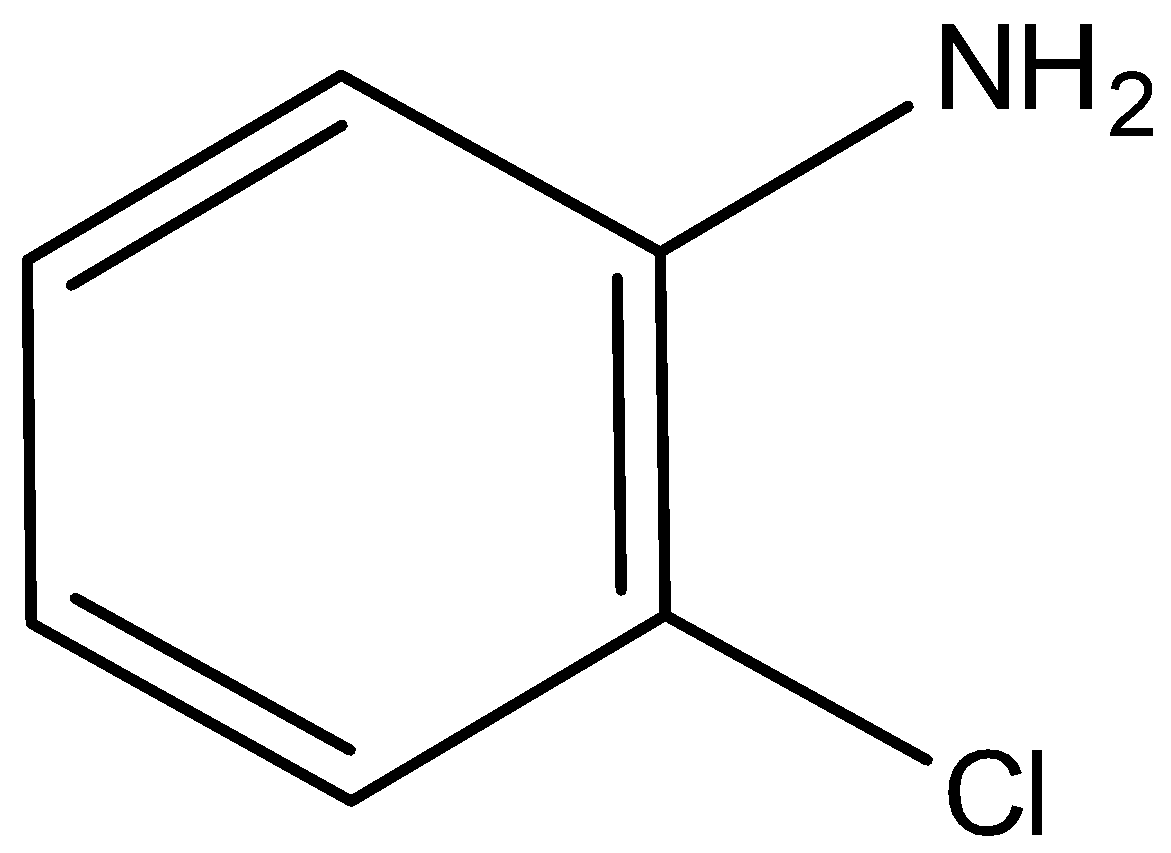
Solution
The reaction given in the above question is a name reaction of organic chemistry. It is known as carbylamine reaction also popularly known as Hofmann’s isocyanide synthesis. Looking into the reaction and mechanism of carbylamine reaction we can answer the above question.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction in the question is known as the carbylamine test or Hofmann’s isocyanide synthesis. The reaction includes amine functional group, chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide. When chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide react with amine, they form a compound containing isocyanate functional groups with potassium chloride and water.
R−NH2+CHCl3+3KOH→RNC+3KCl+3H2O
This reaction is very important in the organic chemistry of amines because it is a test for the identification of primary amines. When primary amine is reacted with chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide, it forms a foul smell by the formation of isocyanide. This foul smell is not obtained in the reaction with secondary and tertiary amine because there is no formation of isocyanide.
Carbylamine reaction mechanism:
An intermediate is created when there is a dehydrohalogenation( removing hydrogen and a halide atom)of chloroform. The intermediate is popularly known as dichlorocarbene. This intermediate is highly reactive and it is electrophilic in nature therefore it attacks the nucleophilic in nature nitrogen atom present in the amine functional group. Hence there is the elimination of hydrochloric acid which leads to the formation of isocyanide compounds.
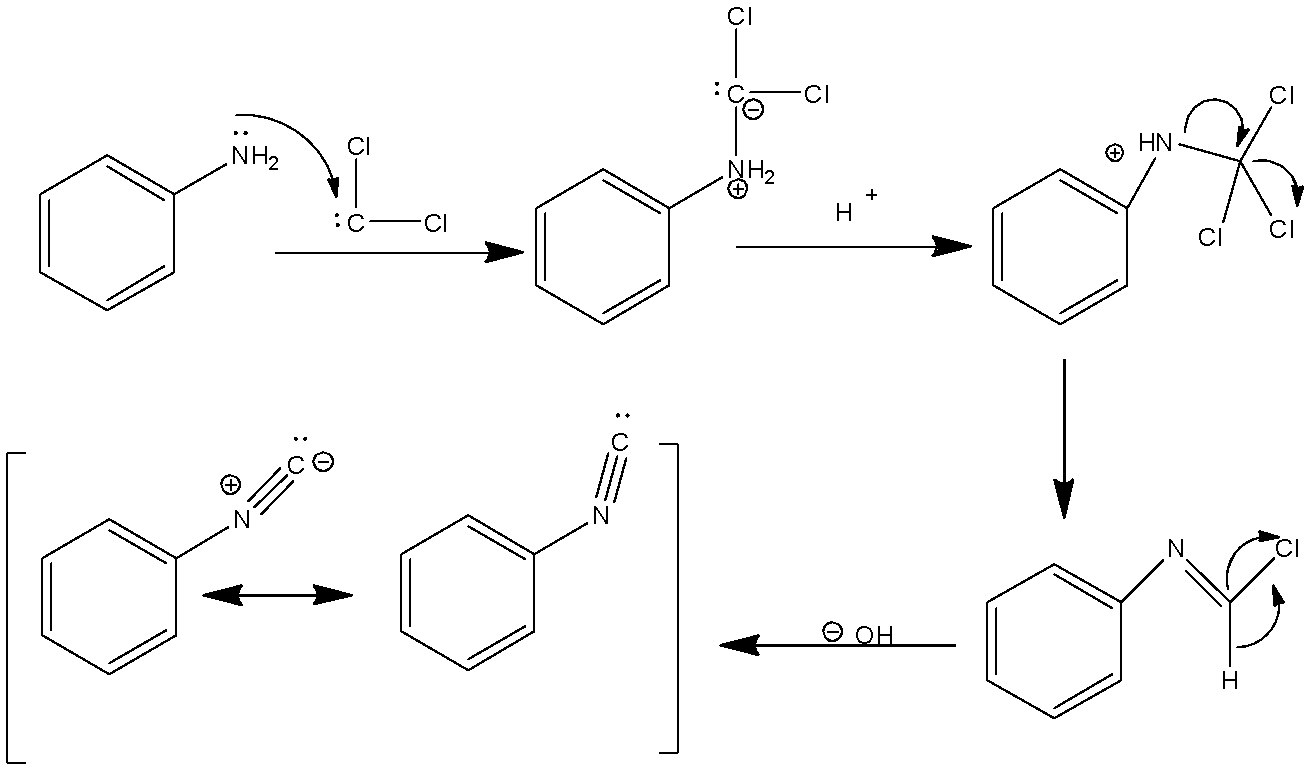
Therefore in the reaction given in the question, we obtain an isocyanide that is phenyl isocyanide.
Note: Note that carbylamine reaction can be used in two ways. The first main important role of the Carbylamine reaction is to predict the presence of primary amine in the solution. The second important role is to form isocyanide from primary amines with the help of chloroform, an alcoholic potassium hydroxide(base).
